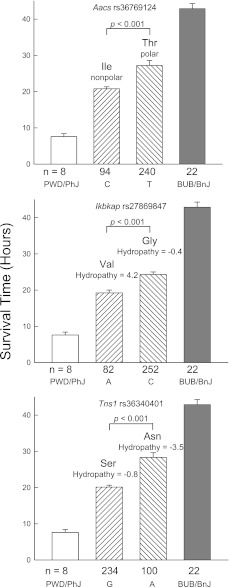
Figure 2.
Assessment of the phenotypic difference in survival times between polar sensitive PWD/PhJ and resistant BUB/BnJ murine strains produced by nonsynonymous single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) associations in exemplary candidate genes. The mean survival time was determined for mice carrying either allele (n = number of mice with either allele, as indicated below the abscissas). The difference between these groups was then compared with the difference of the means of polar sensitive PWD/PhJ (n = 8 mice) and resistant BUB/BnJ (n = 22 mice) murine strains exposed to 45 ppm chlorine (total = 364 female mice). The SNP identification “rs” number is indicated in each histogram. The predicted amino acid is presented for either allele, with the consequences to side-chain polarity or hydropathy index. Value represent means ± standard errors, and P values indicate the significance of the difference between the allele means as determined by ANOVA, according to an all-pairwise multiple comparison procedure (the Holm-Sidak method). Aacs, acetoacetyl-coenzyme A synthetase; Ikbkap, inhibitor of κ light polypeptide enhancer in B cells, kinase complex–associated protein; Tns1, tensin 1. C = cytosine, T = thymidine, A = adenine, and G = guanine at the SNP position.