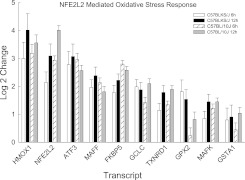
Figure 6.
Transcripts in the enriched nuclear factor erythroid-derived–2–like 2 (NFE2L2, also known as Nrf2)–mediated oxidative stress response pathway in the lungs of C57BLKS/J and C57BL/10J mice after chlorine-induced acute lung injury. Microarrays increased transcripts (significantly different, at P < 0.05, from strain-matched control mice) that were enriched as determined by the logistic regression approach LRpath. Transcripts in this pathway were similar between strains, and included heme oxygenase (decycling)–1 (HMOX1); nuclear factor, erythroid-derived–2–like 2 (NFE2L2); activating transcription factor–3 (ATF3); v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene family, protein F (avian) (MAFF); FK506 binding protein–5 (FKBP5); glutamate–cysteine ligase, catalytic subunit (GCLC); thioredoxin reductase–1 (TXNRD1); glutathione peroxidase–2 (GPX2); v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene family, protein K (avian) (MAFK); and glutathione S-transferase, α 1 (Ya) (GSTA1). Values represent means ± SE (n = 6 female mice/strain/time), normalized to strain-matched control mice (0 hours).