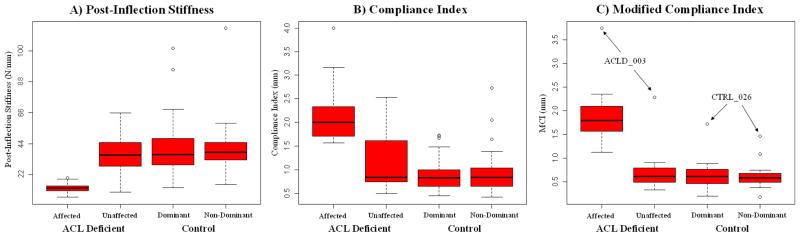
Figure 3.
Differences by limb in distributions between S2 (Fig 3A), compliance index (Fig 3B), and modified compliance index (Fig 3C). ACLD n=15, CTRL n=50. Large variability in the distributions for S2 and the compliance index for healthy limbs (ACLD Side 2, CTRL Side 1, CTRL Side 2) is greatly reduced using the MCI, or the compliance over a 22N interval after curve-inflection. MCI reduces the overlap in distributions between healthy and ACL-deficient limbs. Four of 115 healthy limbs (outliers) demonstrated a false positive test for ACL deficiency based on data from a single limb. False positives can be compared to the contralateral limb as a verification technique, as demonstrated by the subject specific nature of these outliers.