Figure 2. Structure and Function of Podosomes and Invadopodia.
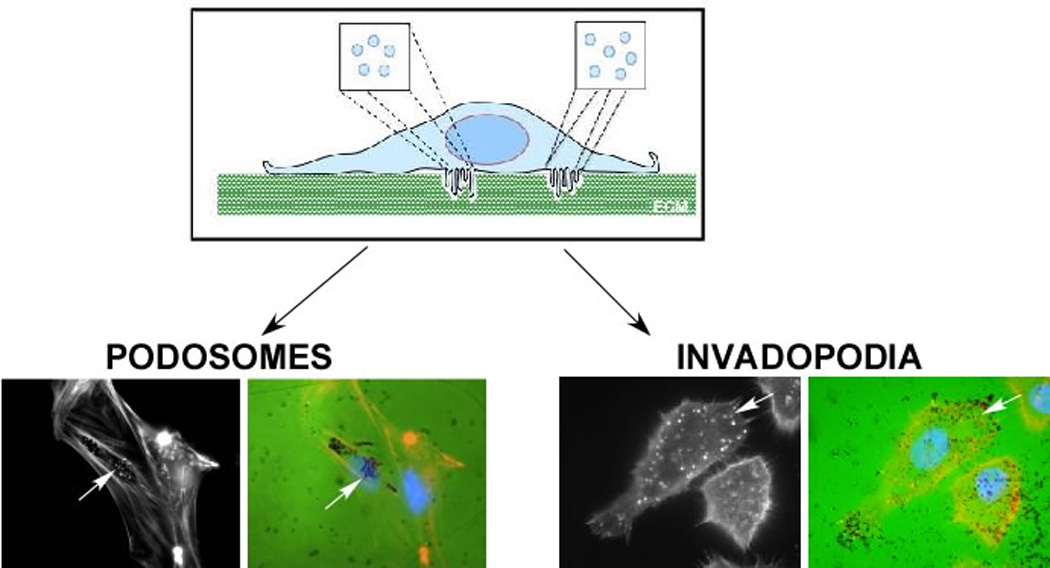
Podosomes and invadopodia are actin rich structures that are formed on the ventral membrane of the cell. These structures are often seen as individual puncta or rosettes that protrude into the extracellular matrix (ECM). Classically, presence of these structures is often confirmed by culturing cells on top of fluorescently-conjugated matrix (FITC-gelatin), staining cells for F-actin and examining co-localization between F-actin puncta and degradation of matrix (black regions). This is demonstrated in vascular smooth muscle cells (podosomes) and SCC61 head and neck squamous carcinoma cells (invadopodia) as indicated by arrows.
