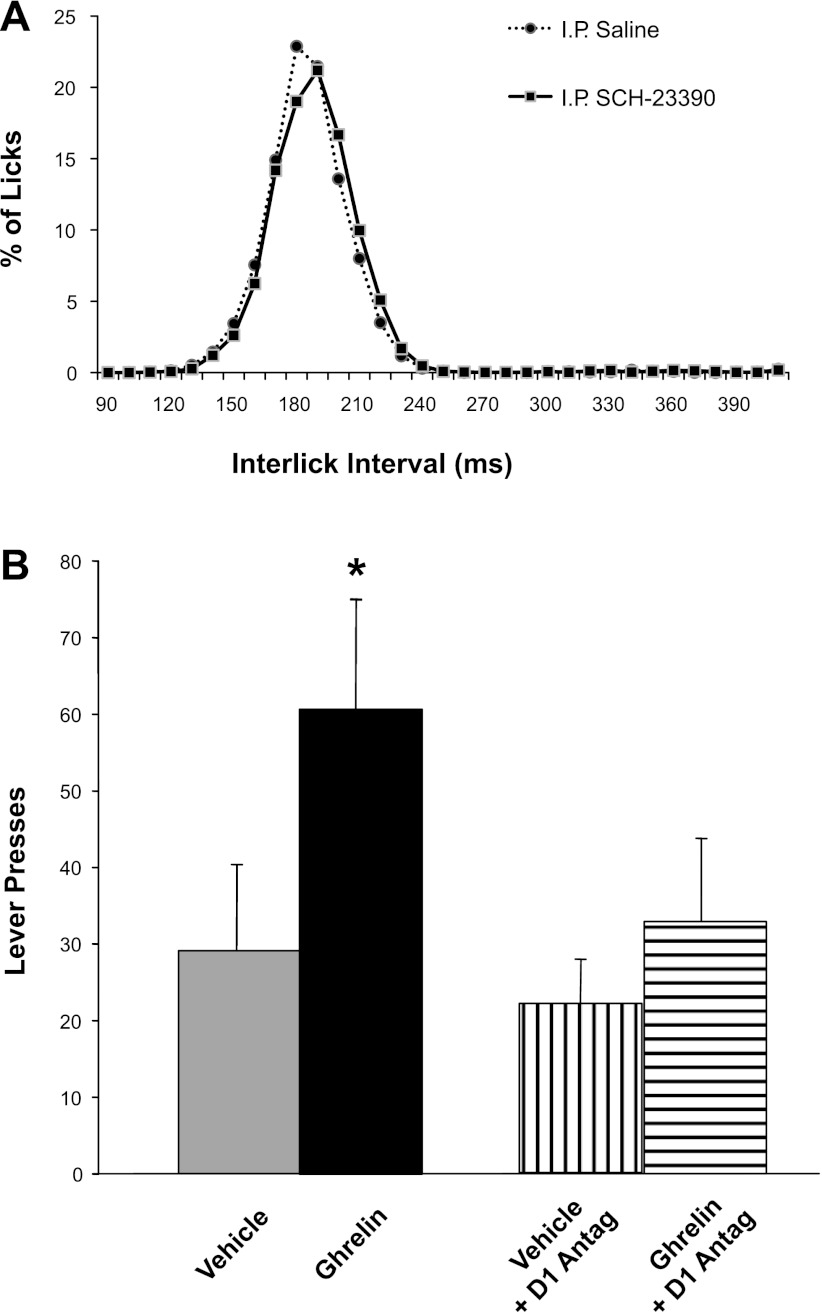
Fig. 6.
Effects of intraperitoneal administration of the D1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH-23390 (50 μg/kg ip) on fine motor behavior in the tongue (interlick interval distribution) and progressive-ratios self-administration of food. A: interlick interval distribution during consumption of a liquid meal (Intralipid, Baxter Healthcare) was comparable after administration of vehicle or SCH-23390. Thus, this dose of D1-antagonist did not cause any gross motor impairment in licking that could confound the assessment of the compound's impact on progressive ratios responding shown in B. B: effects of SCH-23390 on progressive-ratios responding. Prior administration of SCH-23390 eliminated ghrelin-induced increases in progressive-ratio bar-press responding. The same intervention had no effect on baseline bar pressing (i.e., there was no difference between vehicle injections with vs. without SCH-23390). These results indicate an involvement of dopamine D1 receptor signaling in the food-related motivational effects of ghrelin.