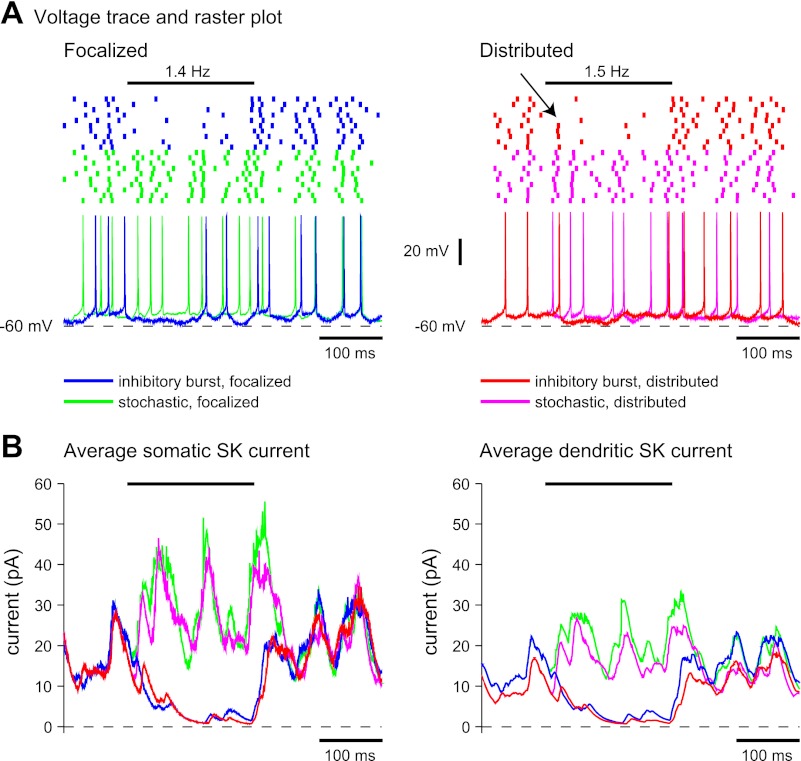
Fig. 8.
Response to an inhibitory input burst for focalized or distributed input in the model. The horizontal bar above the raster plots indicates the duration of the input burst. The mean firing rate in the control trials was 26.9 Hz for focalized inputs and 23.0 Hz for distributed input. Before the start of the input burst, spike times in the control and patterned trials were exactly the same. A: a 50% increase in the inhibitory input rate caused a nearly complete suppression of spiking to a 1.4-Hz spike rate for focalized input (left) and to a 1.5-Hz spike rate for distributed input (right). For distributed dendritic input, the onset of spike suppression was not as complete during the first 25 ms, and in some trials spikes were still present early during the inhibitory period (arrow). B: during the inhibitory burst, the magnitude of the SK current strongly decreased due to the absence of spikes but returned to the control trajectory when the burst ended. The pattern of SK activation was similar for both the focalized and distributed input conditions. The average SK current across different noise conditions is shown.