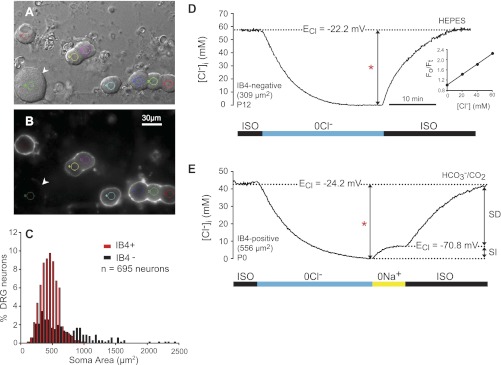
Fig. 4.
Intracellular Cl− concentration ([Cl−]i) in DRG neurons of identified phenotype. A: differential interference contrast (DIC) image of acutely dissociated rat DRG neurons (P12). B: isolectin B4 (IB4) fluorescent labeling (FITC) of the cells in A. IB4 appears as a white halo around the surface of the cells that bind it. IB4+ cells are of small size [soma cross-sectional area (CSA) ∼450 μm2]. The only large neuron (1,506 μm2) in the field (arrowhead) is IB4−. Small colored circles in A and B delimit the digital pinhole areas from which MQAE fluorescence was collected. C: frequency distribution of dissociated DRG neurons according to cell size (soma area) and IB4 labeling (n = 695). Red bars represent IB4+ cells and black bars IB4− cells. All IB4+ cells are small or medium size, whereas IB4− cells are small or medium to large size (note skewed tail toward large sizes). D: typical intracellular Cl− transient in response to isosmotic removal and readdition of external Cl− used to measure basal [Cl−]i and Cl− equilibrium potential (ECl) in single-identified DRG neurons loaded with MQAE. The neuron was initially equilibrated in isosmotic control solution (ISO). On removal of external Cl− (0 Cl−), the cell was depleted of Cl−. On restoration of external Cl− (131 mM), [Cl−]i recovered to initial values. All the solutions in this group of cells were buffered with HEPES. The basal [Cl−]i (measured as the difference indicated by the bracketed arrow labeled with a red asterisk) in this neuron (IB4−, 309 μm2 CSA, P12) was 60 mM, and ECl = −22.2 mV. Inset: calibration plot of relative MQAE-emitted fluorescence (Fo/Ft) as a function of [Cl−] in the calibration solutions. The slope of this relation is the Stern-Volmer constant (Ksv in Eq. 1), which in this case was 19.2 M−1. E: changes in [Cl−]i following isosmotic removal and readdition of external Cl−, in the absence and presence of external Na+. All the solutions were buffered with CO2/HCO3−. On removal of external Cl− (0 Cl−), the cell (IB4+, CSA 556 μm2, P0) was depleted of Cl−. On restoration of external Cl− (113 mM) in the absence of external Na+ (0 Na+) there was a small increase in [Cl−]i that reached steady state at the expected electrochemical equilibrium (ECl = −70.8 mV; [Cl−]i = 7.2). This is the sodium-independent (SI) component of Cl− accumulation. On exposure to the ISO control solution, [Cl−]i recovered to initial values (44 mM, measured as indicated by red asterisk; ECl = 24.2 mV). The later recovery is the sodium-dependent (SD) component of Cl− accumulation. Scale bar in B applies to A.