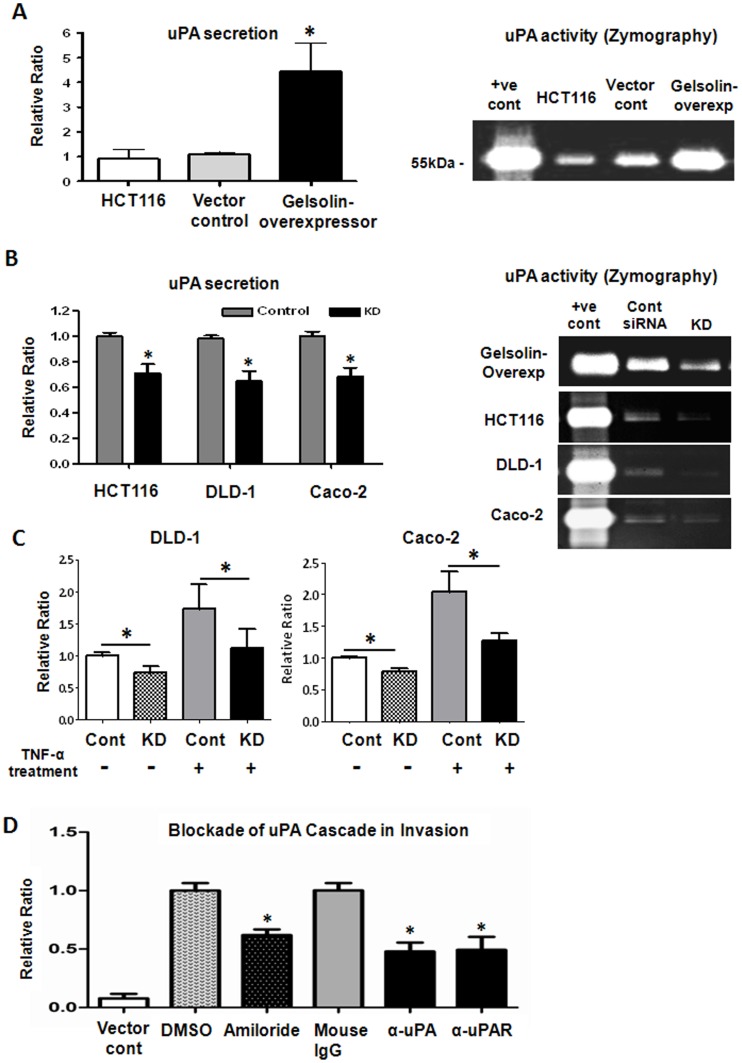
Figure 5. Gelsolin increases uPA secretion of colorectal tumor cells and enhances invasion via the urokinase-type plasminogen (uPA) cascade.
(A) Increased gelsolin in HCT116 cells augmented the secretion and activity of uPA. The levels of secreted uPA by cells cultured for 48 hours in serum-free conditions were detected in the supernatant using ELISA. Gelsolin-overexpressing HCT116 cells secreted significantly higher uPA levels compared to control cells (left), which correlated with higher uPA enzymatic activity, as evident from uPA zymographic analysis using 16-hour serum-free conditioned media of cells (right). (B) Knockdown of gelsolin (KD) reduced the secretion of uPA. Gelsolin-overexpressing HCT116, wildtype HCT116, DLD-1 and Caco-2 cells were treated with gelsolin siRNA or control siRNA for 24 hours prior to culture under serum-free conditions for a further 48 hours. The levels of secreted uPA were detected using ELISA (left). Zymographic analysis indicated that uPA activity in the 3-hour conditioned media of the colorectal tumor cells was reduced 48 hours after gelsolin siRNA knockdown treatment (right). (C) Gelsolin expression affects TNF-α-stimulated uPA secretion in colorectal cancer cells. DLD-1 and Caco-2 cells were treated with gelsolin siRNA (KD) or control siRNA (Cont) for at least 24 hours and serum-starved overnight prior to incubation with 5 ng/mL (DLD-1) and 10 ng/mL (Caco-2) TNF-α for 24 hours. The levels of secreted uPA in the supernatant of cultured cells were detected using ELISA. uPA secretion was effectively stimulated by TNF-α in DLD-1 and Caco-2. However, siRNA knockdown of gelsolin significantly attentuated TNFα-stimulated uPA levels in the colorectal cancer cell lines. (D) Inhibition of uPA cascade attenuates the invasion of gelsolin-overexpressing HCT116 cells through matrigel. Gelsolin-overexpressing cells were treated with either 50 µM amiloride, 200 µg/mL of function-blocking anti-uPA or 80 µg/mL of anti-uPAR antibodies and examined for changes in invasive potential through matrigel. DMSO treatment and mouse IgG antibody at 200 µg/mL were used as controls to amiloride and the function-blocking antibodies and respectively. Untreated vector control HCT116 was included and normalized to DMSO vehicle control. The anti-uPA and anti-uPAR as well as amiloride treatments significantly attenuated invasion of gelsolin-overexpressing HCT116 cells, indicating that the enhanced invasiveness induced by gelsolin is mediated through the uPA cascade. All data shown are the mean ± standard error of triplicate (ELISA) and duplicate (invasion assay) measurements and are representative of at least two independent experiments. P<0.05 (student’s t test).