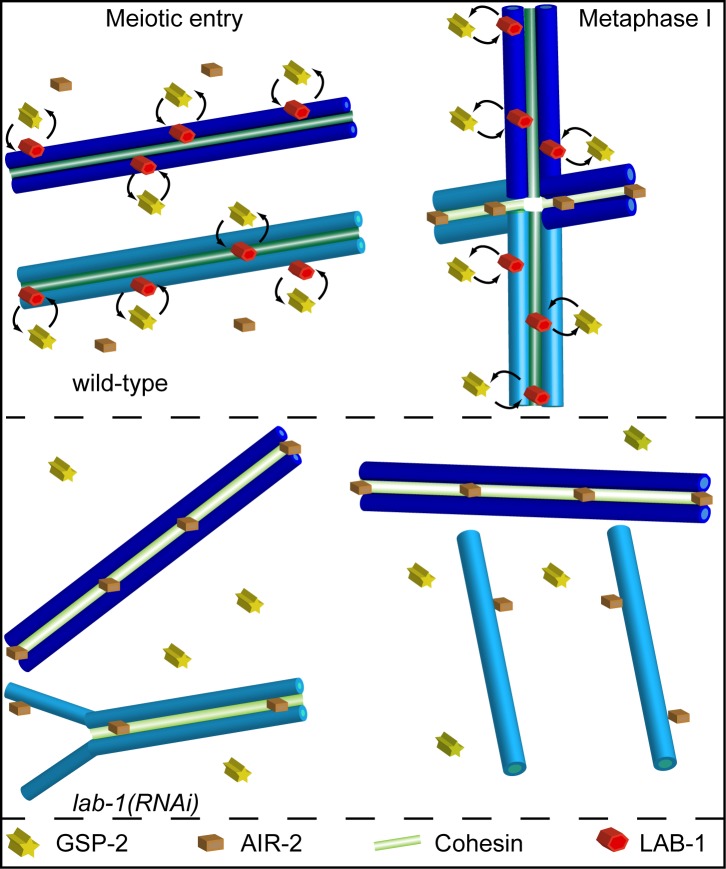
Figure 7. LAB-1 utilizes a similar mechanism to protect SCC during two different meiotic stages.
In wild type, LAB-1 starts associating with the chromosomes at the entry into meiosis and transiently targets GSP-2 to the chromosomes. This targeting antagonizes AIR-2 and maintains SCC. During diakinesis, LAB-1 localizes to the long arms, where it specifically antagonizes AIR-2 and protects REC-8 from premature removal. When lab-1 is depleted, AIR-2 associates with the chromosomes as early as transition zone, and SCC is perturbed. The weakened SCC prevents successful binding of homologs and many reach diakinesis as either univalents or detached chromatids.