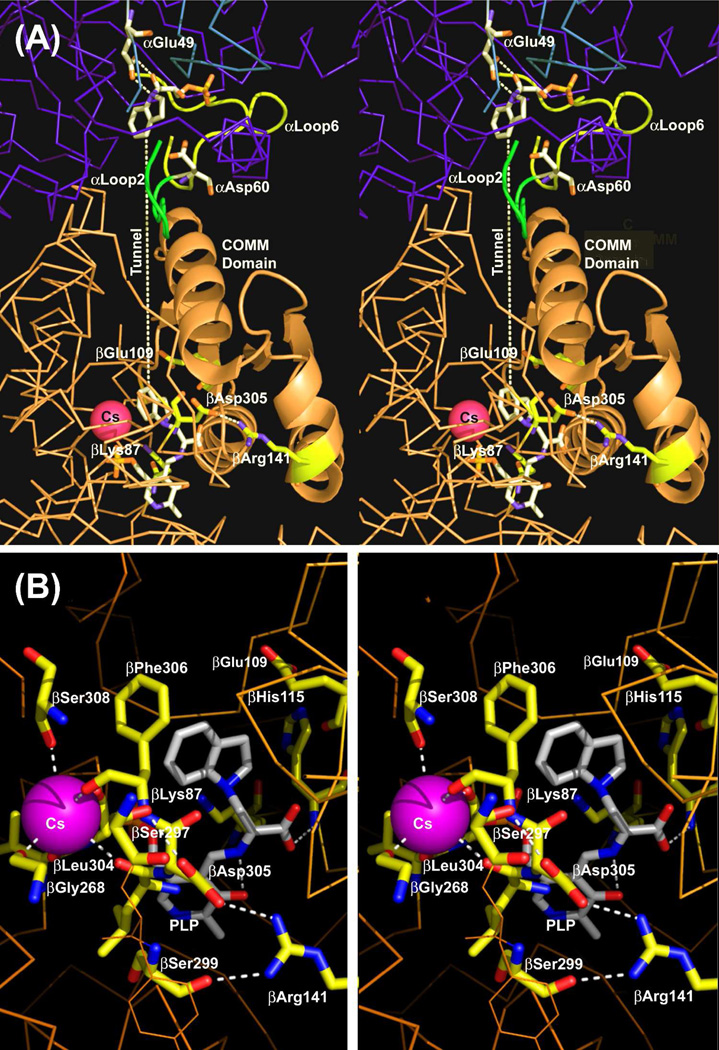
Figure 1.
Stereo over view of the structure of an αβ-dimeric unit of the E(Q)indoline, and details of the β-catalytic site. (A) Stereo view of the catalytic sites of the α- and β-subunits, the MVC site and interconnecting tunnel. The dashed white line indicates the approximate position of the tunnel. The transition state analogue formed by the reaction of indoline with G3P at the α-site and the quinonoid intermediate at the β-site are shown in sticks. Cs+ is shown as a magenta ball. The α-subunit is represented by a backbone structure colored blue, the β-subunit is colored tan. αLoop L2 and αLoop L6 are shown, respectively, as yellow and blue ribbons. The COMM domain is shown in cartoon ribbon, the remainder of the β-subunit in backbone. At the α-site, catalytic residues αGlu49 and αAsp60 and the adduct formed between indoline and G3P are shown in CPK-colored sticks. At the β-site, catalytic residues βLys87 and βGlu109 and the salt bridging residues βArg141 and βAsp305 are shown as sticks with C yellow, N blue and O red. The structure of the indoline quinonoid intermediate is shown in CPK-colored sticks. (B) Stereo view of the β-catalytic site with the PLP-bound indoline quinonoid intermediate shown in CPK-colored sticks. The catalytic residues βLys87 and βGlu109, the βAsp305-βArg141 salt bridge, H-bonding residues βSer299 and βSer297, indole sub-site residues βHis115 and βPhe306 and Cs+ ligands βGly268, βLeu304, βPhe306 and βSer308 are shown in sticks with C yellow, N blue, and O red. Cs+ is shown as a purple ball. H-bonding interactions and coordination bonds to Cs+ are shown as white dashed lines. The β-subunit is represented as orange backbone. Structures are drawn from PDB code 3CEP with PyMOL 1.1r1.