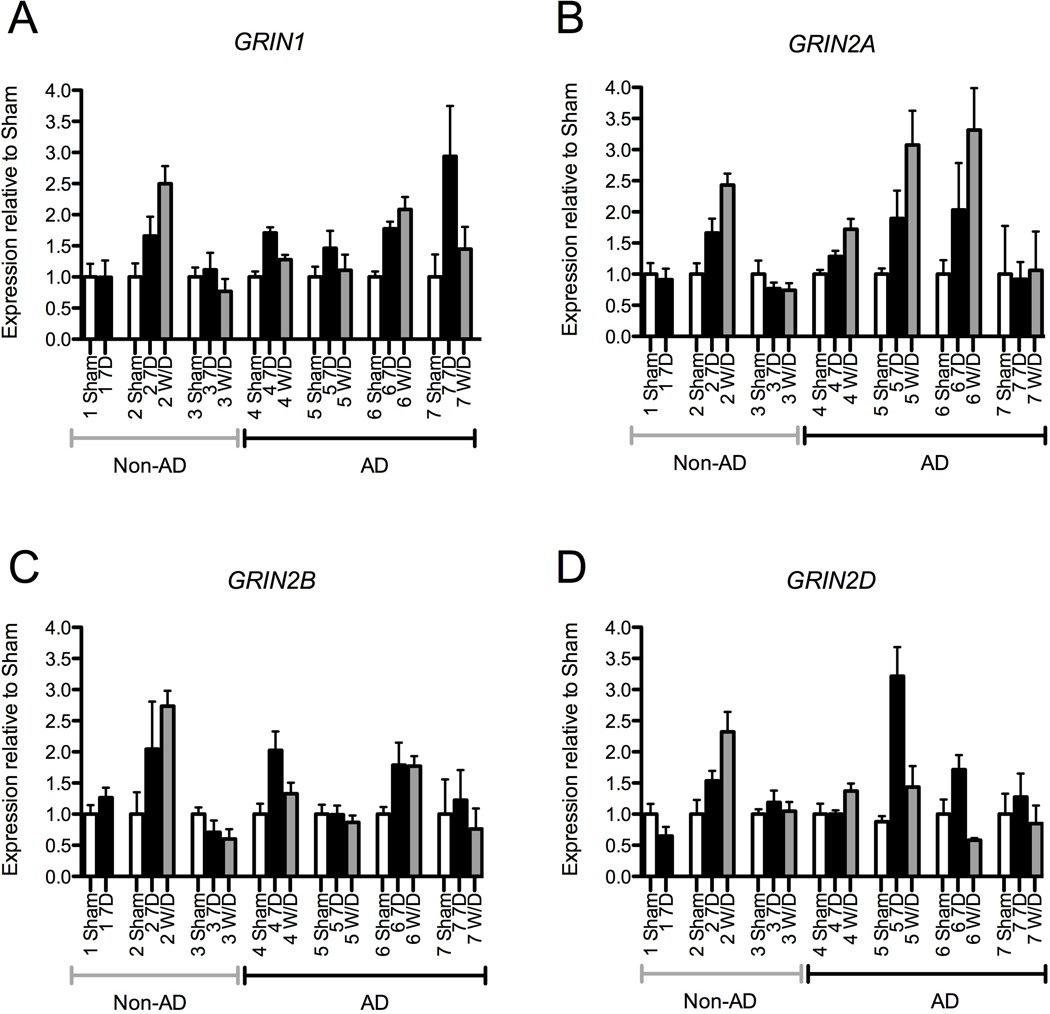
Figure 5. Variability Between Subjects in NMDA Subunit mRNA changes following Alcohol Exposure and Withdrawal.
Individual subject data normalized to each subject’s average sham NMDA receptor gene expression normalized to GUSB. iPS-derived neural cells from non-alcohol dependent (Non-AD) subjects are indicated on the left side of the x-axis, while neural cell generated from alcohol-dependent (AD) subjects are indicated on the right. Only one non-AD subject demonstrated an increase in NMDA mRNA expression following 7 days of alcohol exposure. In contrast, under these conditions, all four AD subjects demonstrated increased expression of GRIN1, which returned to baseline levels in three of the four subjects. Three AD subjects demonstrated increased GRIN2A expression, which continued to increase after 24 hours of withdrawal in all three subjects. Two AD subjects showed increases in GRIN2B and GRIN2D expression; with the exception of GRIN2B in one AD subject, these changes returned to baseline after withdrawal. (Symbols: open bars − sham condition; solid bars − 7-day of alcohol exposure; gray bars − 7-day alcohol + 24-hour withdrawal; error bars represent SEM).