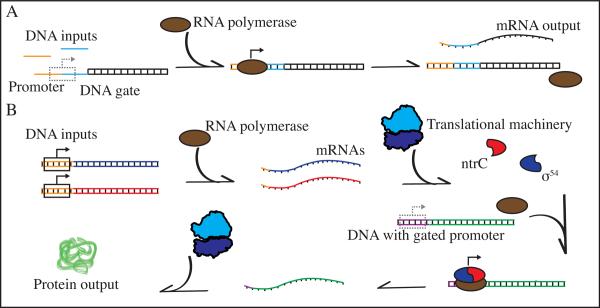
Figure 3.
Sample AND gate implementation in hybrid and complete systems. (A) Hybrid systems may use DNA, RNA, or small molecule inputs and outputs. Here, an incomplete promoter (dashed box) is bound by two ssDNA inputs that complete the promoter region. The polymerase enzyme (brown) then binds and transcribes an mRNA output. (B) Complete systems have a diverse array of possible inputs and outputs. Here, two DNA input signals with intact promoters (solid box) are transcribed into mRNA and translated into functional protein products ntrC (red) and σ54 (blue). These protein products then bind to a polymerase and allow it to transcribe a gated promoter (dashed box), leading to production of a protein output [55].