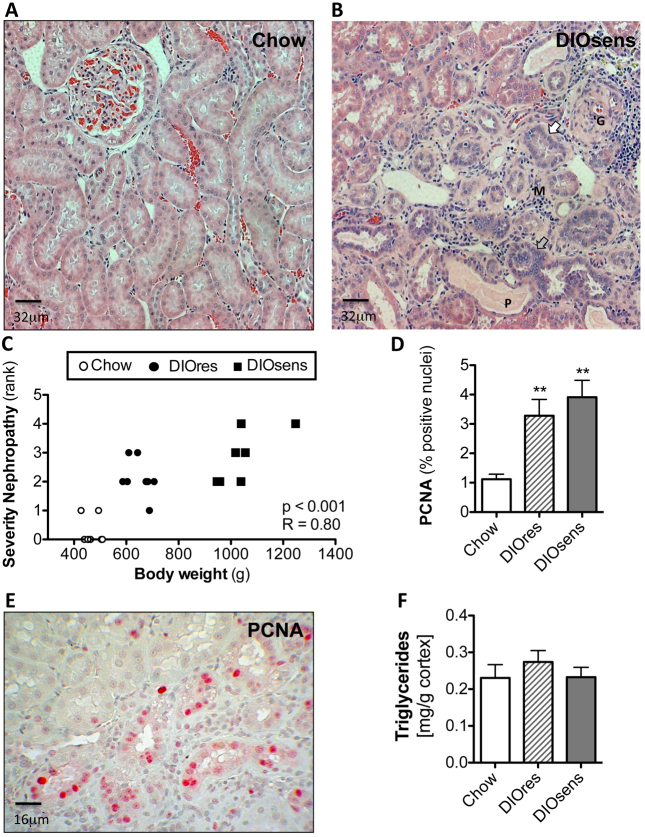
Fig. 2.
Increased severity of renal pathology in DIO rats. (A) Representative H&E-stained paraffin section of a kidney from a chow-fed control animal without visible pathological changes. (B) Pronounced nephropathy in DIOsens rats was observed, including glomerulosclerosis (G), proteinaceous casts (P), infiltration of monocytes (M), slightly basophilic regenerating tubules with thickened basal membrane (white arrow) and simple tubular hyperplasia (grey arrow). (C) Spearman rank correlation of body weight with the severity of overall renal pathology. (D) PCNA labeling indices (LI) of chow-fed, DIOsens and DIOres rats. LI were determined for proximal tubules within randomly chosen fields of the outer or inner cortex. Within both regions at least 1000 positive and negative nuclei were counted. LI were tested for significance using one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post tests for multiple comparisons. **P<0.01. (E) Representative image of a PCNA-stained kidney section from a DIOsens rat. Nuclear PCNA staining represents cells after G1-S transition. (F) Absence of renal triglyceride accumulation in kidneys of DIO rats.