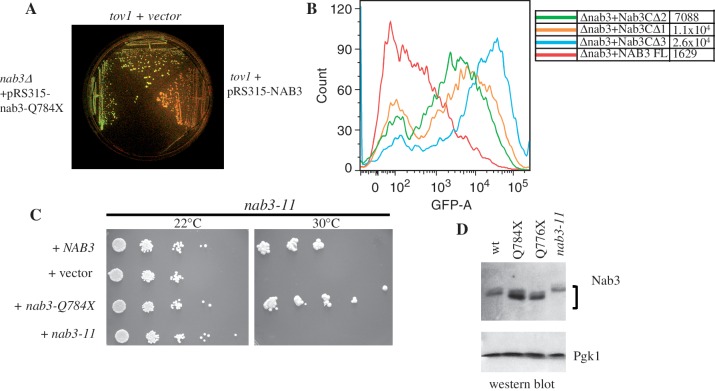
Figure 8.
Testing of wild-type and mutant NAB3 function. (A) tov1 strains containing the GAL-IT-GFP reporter plasmid and either an empty control vector control (DY3018; top sector) or a plasmid with the NAB3 gene (DY3019; right sector), were grown on galactose along with a strain (DY2240; left sector) deleted for chromosomal NAB3 and containing a plasmid expressing the tov1 mutation of NAB3 (nab3-Q784X). The plate was photographed under blue light to detect GFP fluorescence. (B) A yeast strain lacking its chromosomal copy of NAB3 and containing the GAL-IT-GFP reporter plasmid was transformed with a second plasmid containing the wild-type (‘NAB3FL’; DY3036), the Δ3 (‘nab3CΔ3’; DY3038), the Δ2 (‘nab3CΔ2’; DY3060) or the Δ1 (‘nab3CΔ1’; DY3061) derivatives of NAB3, as indicated. Cells were grown in the presence of galactose and analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) A strain with the nab3-11 allele was transformed with a plasmid containing either the wild-type NAB3 (DY30109), the tov1 allele nab3-Q784X (DY3012), the nab3-11 allele (DY3013) or an empty vector (DY3011). Cultures were serially diluted 10-fold and the dilutions were spotted on selective medium for growth at 22°C or 30°C, as indicated. (D) Western blot for Nab3 in wild-type (DY1514F) and the indicated mutant strains (1A1F = ‘nab3-Q784X’, 4A1F = ‘nab3-Q776X’, DY30229 = ‘nab3-11’). Pgk1 served as a loading control. The nab3-11 strain was grown at the permissive temperature of 22°C.