Figure 3.
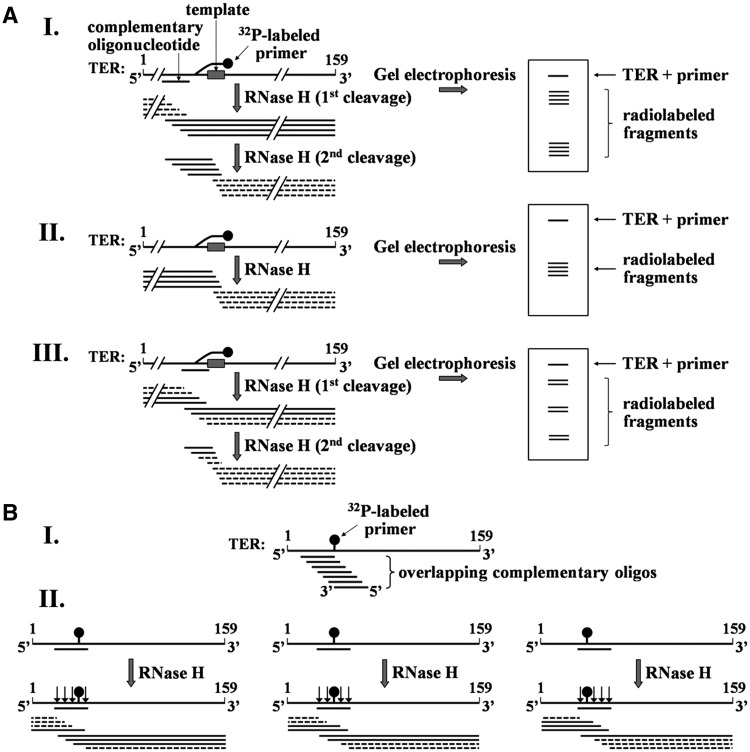
Strategies for mapping the cross-link sites in TER. (A) Schematic illustration of the initial mapping procedure. Purified cross-linked DNA primer–TER molecules are hybridized with an oligo complementary to a region of the RNA. The hybrids are digested with RNase H and the products are resolved in 8% polyacrylamide gel containing 7 M urea and 38.5% formamide, followed by phosphorimaging of the gel. Note that only the fragments including solid lines are radioactively labeled. I. RNase H digestion (first cleavage) of hybrid generated by oligo complementary to a region in the RNA that does not include the cross-link site. RNase H (second cleavage) also cleaves the fragments generated by the first digestion within the hybrid formed in these fragments between the primer and the RNA template region. II. An RNase H digestion assay performed in the absence of complementary oligo. Cleavage occurs in the hybrid formed with the primer. III. RNase H digestion performed in the presence of complementary oligo that overlaps with the cross-link site. (B) Strategy for mapping the cross-link site at a high resolution. I. A series of overlapping complementary oligos are employed. These oligos are chosen to cover the region found by the initial mapping to contain the cross-link site. II. Illustration of cleavage patterns obtained with oligos complementary to the left, middle and right sides of the cross-link. As shown in Figure 3A-III, a second cleavage of fragments including the cross-linked site may also occur in these assays within RNA–DNA hybrids formed between the primer and the template region in TER. To save space, this second cleavage is not shown here. A detailed explanation of this procedure is presented in the text.