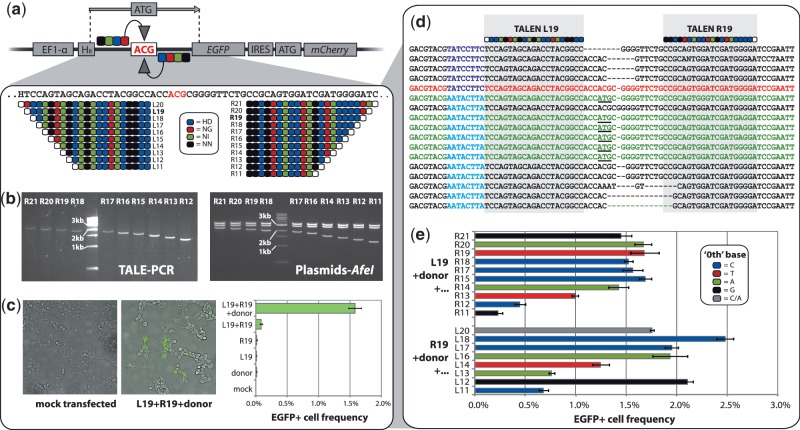
Figure 2.
Testing activity of TALEN variants on a human cell reporter system. (a) To generate a TALEN activity reporter system we integrated a barcoded (H8, H = A/C/T) defective EGFP gene carrying a non-functional ACG start codon into the genome of 293 T cells. Gene editing by a 75-nt donor oligonucleotide stimulated by a TALEN-mediated double-strand break near the target site should correct the start codon and rescue EGFP expression. We designed 21 length variants of TALENs designed to flank the defective site. TALEN RVD sequences are shown. White monomer circles represent ‘0th’ positions of the DNA target sequence bound by the TALE N-terminus. (b) Post-elution PCR products of the ligated right TALE domains (for R11 see TAL-11, Figure 1b) and AfeI digestions of corresponding assembled and sequence-verified TALEN plasmids. (c) Epifluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry results after transfection of the reporter cells with the L19/R19 TALEN pair and the donor oligonucleotide. (d) Gene editing events (green sequences, functional start codon underlined) were confirmed by sequencing of the target site in EGFP+ cells, with widespread NHEJ (black sequences) also observed (red = unmodified sequence). Reporter barcodes (blue) identify from which of two genomic reporter copies each sequence is derived. (e) EGFP rescue activity of all successfully synthesized TALEN length variants. Each TALEN was transfected together with the donor and either L19 or R19, whichever was relevant. Bar colors indicate the DNA base located at the ‘0th’ position for each TALEN tested. Error bars show standard error (n = 3 for all).