Figure 2. Plasma adrenaline (upper panel) and noradrenaline (lower panel) prior to (−15 min) and during (0–180 min) normoxia (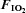 = 0.21) and hypoxia (
= 0.21) and hypoxia (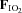 = 0.11), with and without sympathetic inhibition (48 h transdermal clonidine), during measurement of insulin sensitivity via the hyperinsulinaemic euglycaemic clamp.
= 0.11), with and without sympathetic inhibition (48 h transdermal clonidine), during measurement of insulin sensitivity via the hyperinsulinaemic euglycaemic clamp.
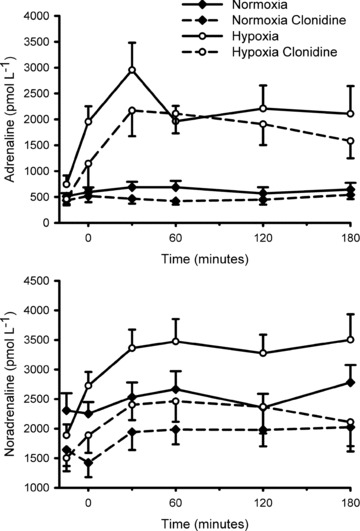
The area under the noradrenaline curve (relative to the normoxia response) was increased with hypoxia (137 ± 13%; P = 0.02); clonidine prevented the hypoxia induced increase (94 ± 14%; P = 0.43). The area under the adrenaline curve (relative to the normoxia response) was appreciably increased in hypoxia (371 ± 40%; P < 0.001). Clonidine did not affect the hypoxia induced increase in adrenaline (346 ± 82%; P < 0.001). Data are means ± SEM.
