Figure 13. Proposed step-by-step trigeminal pathway initiating locomotion.
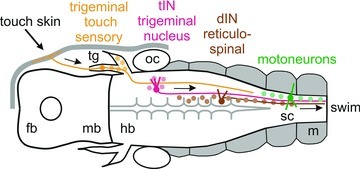
Dorsal view diagram of the tadpole head showing the elements of the trigeminal swim-initiating pathway (arrows): (1) local stimulation of the head skin excites a few touch-sensitive trigeminal sensory neurons (<5); (2) these directly excite and recruit the whole tIN population (∼20); (3) tINs directly excite the reticulospinal hindbrain dINs which are electrically coupled so firing in a few recruits the whole dIN population (∼160); (4) dIN firing initiates rhythm generation and drives all the spinal neurons active during swimming, including motoneurons (∼270); (5) motoneuron firing (vr) drives the swimming muscles. fb, forebrain; hb, hindbrain; mb, midbrain; m, muscles; oc, otic capsule; sc, spinal cord; tg, trigeminal ganglion.
