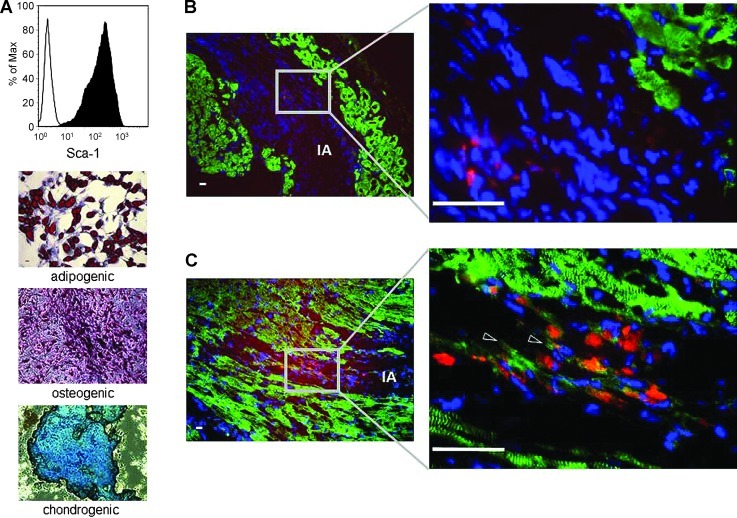
FIG. 6.
Cardiomyogenic differentiation of murine mesenchymal stem cells (mMSCs) in vivo. Flow cytometric analysis showed that mMSCs are highly positive for Sca-1 (A; line histogram shows isotype-matched rat IgG2a antibody control staining, filled histogram shows specific anti-Sca-1 antibody staining). mMSCs could be differentiated into adipocytes (fat droplets stained in red), osteocytes (alkaline phosphatase stained in pink/violet), and chondrocytes (mucopolysaccharides are stained in blue to bluish-green) (A). Fourteen days after infarction, the infarcted area (IA) could be identified by the absence of vital alpha actinin-positive cardiomyocytes (B, C). Fourteen days after transplantation of Sca-1+ multipotent mMSCs into the infarcted heart, the PKH-positive mMSCs could be detected exclusively in the IA indicating homing and survival of mMSCs in the IA (B, C). In most of the analyzed sections the transplanted mMSCs were negative for alpha actinin (B); however, few mMSCs expressed alpha actinin, indicating a possible functional cardiomyogenic differentiation of the minority of the transplanted mMSCs in vivo (C). Alpha actinin: green; PKH26-labeled mMSCs: red; DAPI: blue; shaped arrowheads: mMSCs expressing alpha actinin; scale bars: 20 μm.