Figure 1.
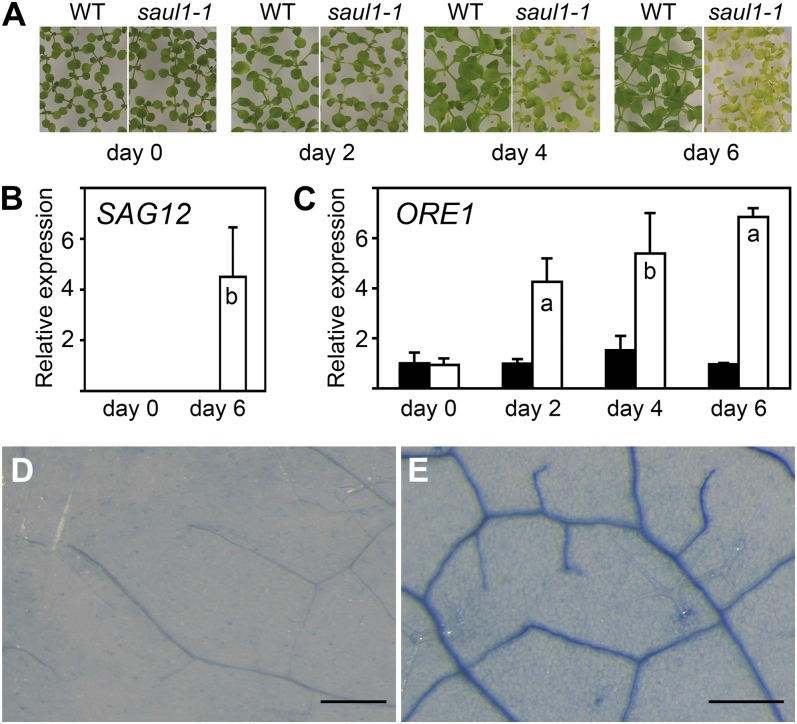
Premature turning on of the switch for age-dependent cell death in saul1 seedlings. A, Senescence phenotype of saul1-1 mutants. Wild-type (WT) and saul1-1 plants were grown for 12 d at 60 µmol m−2 s−1 photon flux density followed by growth for 2, 4, and 6 d at 20 µmol m−2 s−1 photon flux density. Yellowing of leaves appears as a visible symptom of senescence. B, SAG12 transcript level in young saul1-1 seedlings. Bars show relative expression of the senescence marker gene SAG12 in wild-type (black bars) and saul1-1 (white bars) plants at the indicated time points (mean ± sd; n = 3) as determined by qPCR. Note that SAG12 transcripts are absent from wild-type seedlings and saul1-1 mutant seedlings without the senescence phenotype. C, Increased ORE1 transcript levels in saul1 seedlings. Bars show relative expression determined by qPCR of the senescence regulatory gene ORE1 in growth kinetics as in A in wild-type (black bars) and saul1-1 (white bars) seedlings at the indicated time points (mean ± sd; n = 3). D and E, Premature cell death in saul1 mutants. Trypan blue staining indicated dead or dying cells in saul1-1 mutant (E) but not in wild-type (D) seedlings. Assayed leaves (n = 16) were less than 20 d old, and identical leaves and leaf areas were chosen for comparison. Bars = 250 µm.