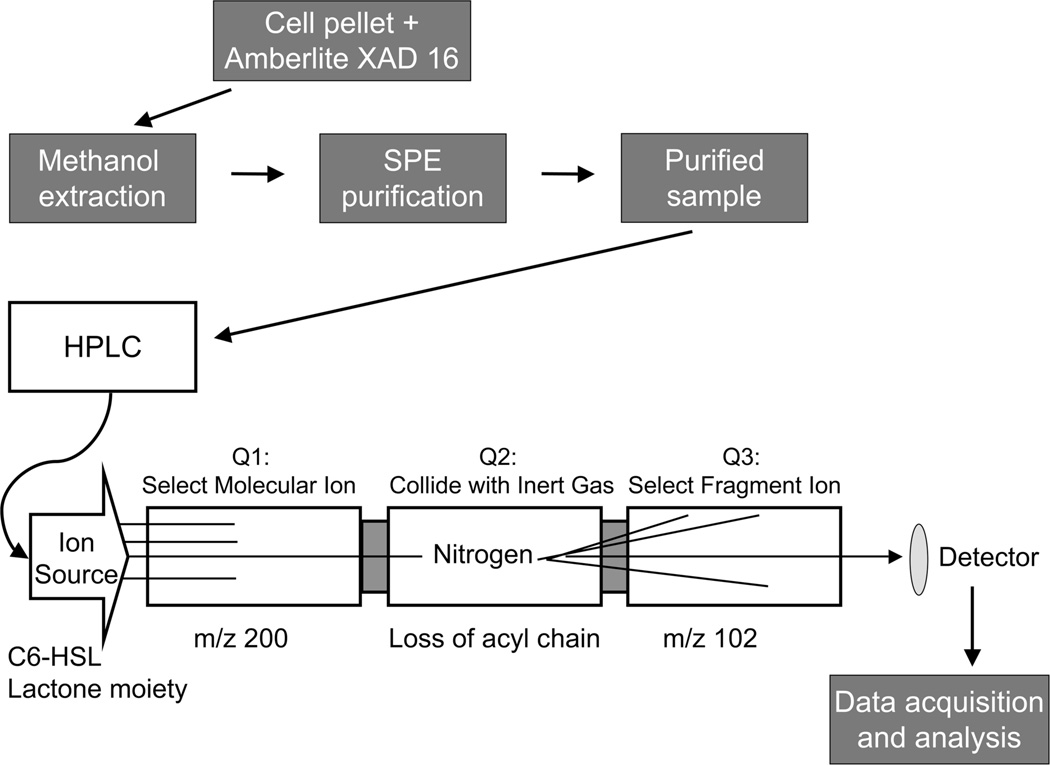
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the methods described in this chapter. The cell cultures were grown in the presence of Amberlite XAD 16, which adsorbs AHLs. In order to extract the AHLs from the resin and cell debris, the harvested pellet from the bacterial culture and Amberlite XAD 16 was re-suspended in methanol and left overnight. The methanol solution was filtered and centrifuged, and then subjected to solid phase extraction to remove any remaining impurities and to concentrate the AHLs. The purified sample was then injected onto the reversed phase HPLC column to separate the AHLs based on their lipophilicity and introduce them into the mass spectrometer. In the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) experiment, the sample was passed through the ion source into Quadrupole1 (Q1), then the selected ions proceeded into Quadrupole 2 (Q2) where they collide with inert gas (nitrogen). After fragmentation, selected ions move into Quadrupole 3 (Q3) and are visualized by the detector. Data were processed by applying standard isotope dilution curves to the analytical data (as in Figures 3 and 4).