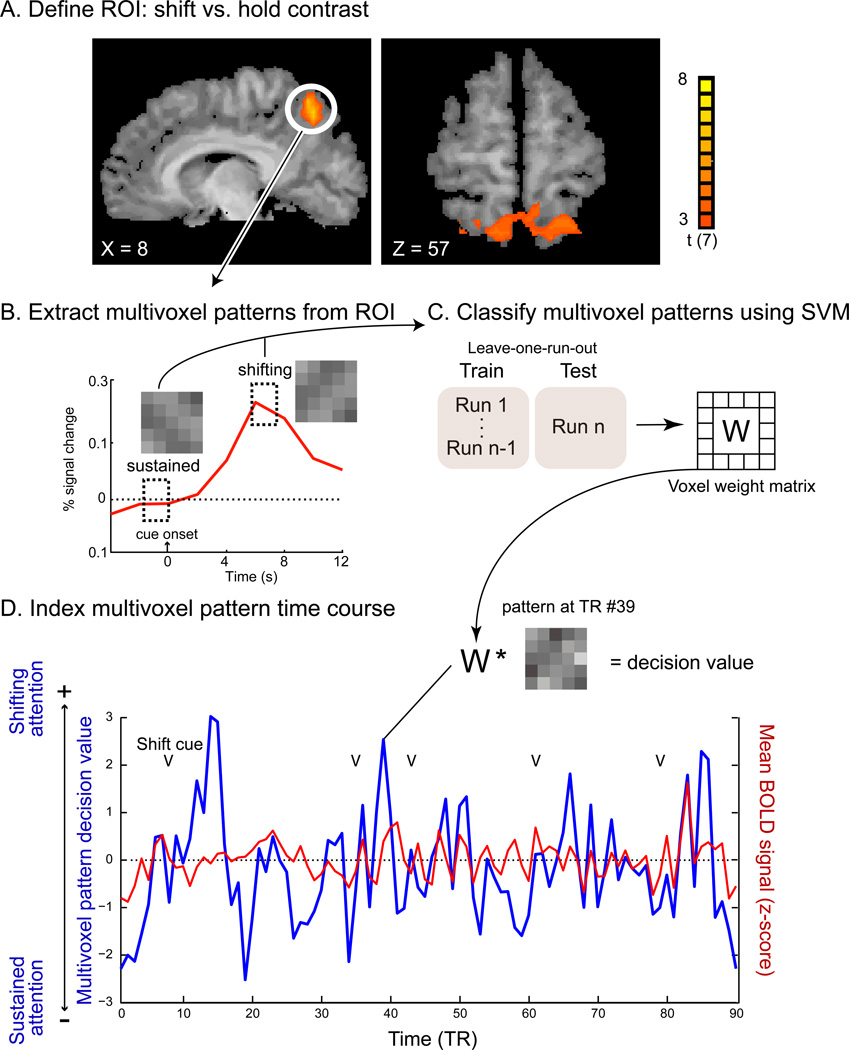
Figure 2.
Multivoxel pattern time course (MVPTC) analysis flow. (A) Shift-related voxels in mSPL as identified by the HRF-based univariate GLM. (B) A schematic illustration of an event-related average BOLD time course in mSPL time-locked to shift cues. The dashed rectangles indicate the time windows that were used to extract multivoxel patterns associated with sustained attention and shifts of attention, respectively, during classifier training. (C) An SVM classifier was trained to discriminate patterns associated with shifts of attention vs. sustained attention and tested using a leave-one-run-out protocol. (D) An example of an mSPL MVPTC (the SVM multivoxel pattern decision value at each time point, in blue) and mSPL mean BOLD time course (expressed as a z-score, in red) from a single run of one representative participant. Arrows mark the onset of shift cues (e.g., sLR or sRL).