Figure 7. Activated Vγ9Vδ2 T cells are still able to induce maturation of Brucella-infected DCs even when they are added 24 h p.i.
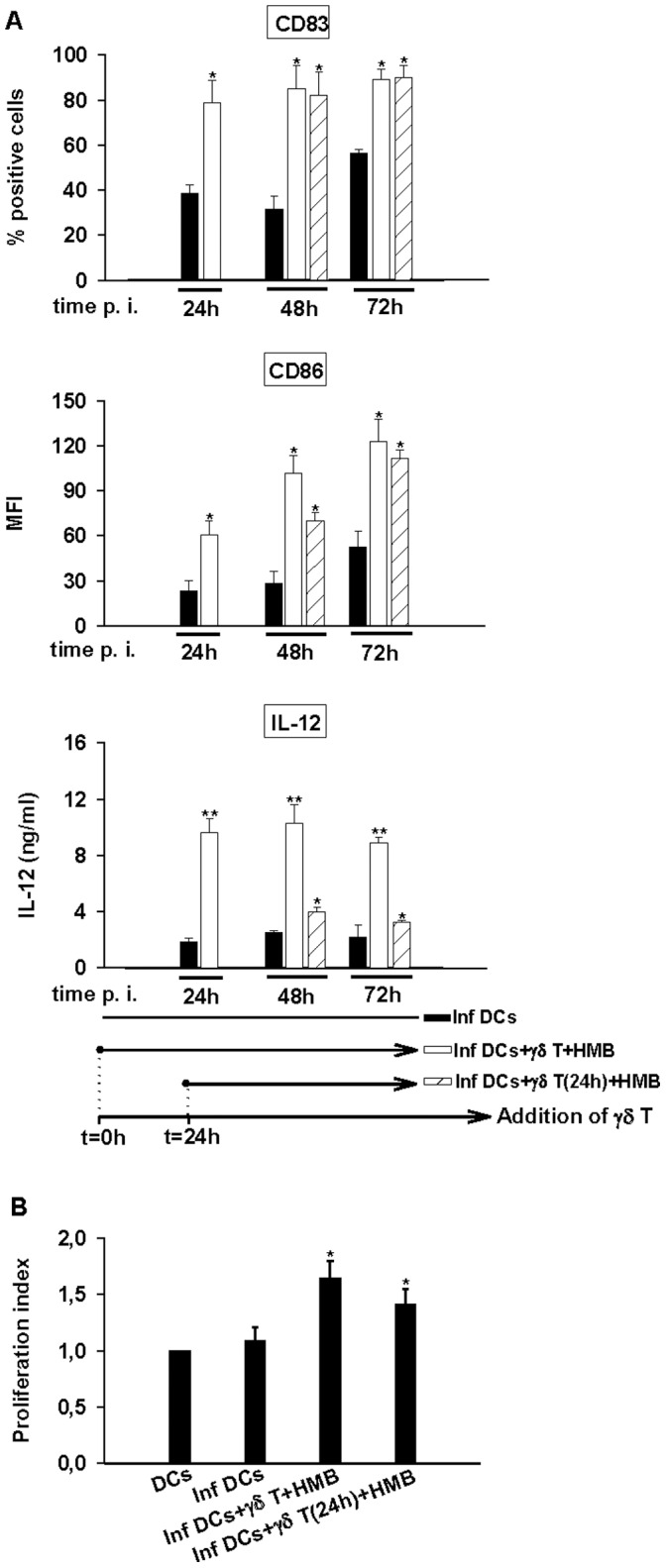
A/Brucella-infected DCs (MOI = 20) were cultured alone or in the presence of stimulated (0.2 nM HMB-PP) Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. Vγ9Vδ2 T cells were added to DCs 1 h or 24 h p.i. At 24 h, 48 h and 72 h p.i., supernatants were collected and cells were stained. CD83 and CD86 expression analysis were realized on CD1a+ cells. IL-12 was assessed by ELISA test in the collected supernatants. Data shown are the mean +/− SD of triplicates and representative of three independent experiments performed with cells from different donor. A significant difference between infected DCs in the presence or not of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells was calculated by using Student’s t test and is indicated by (*) where p<0. 05 and (**) where p<0.01. (B) Brucella-infected DCs (MOI = 20) were cultured alone or in the presence of stimulated (0.2 nM HMB-PP) Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. Vγ9Vδ2 T cells were added either 1 h or 24 h p.i. In all cases, CFSE-stained naive CD4+ T cells were added 24 h p.i. with DC/T cell ratio 0.1. After 5 days, CD4+ T cell proliferation was analyzed by flow cytometry and the proliferation index was calculated by comparison with non-infected cells. Data shown are the mean of duplicates +/− SD of three independent experiments performed with cells from different donors. Statistical difference is calculated by comparison with Brucella-infected DCs by using wilcoxon rank test and is indicated by (*) where p<0. 05.
