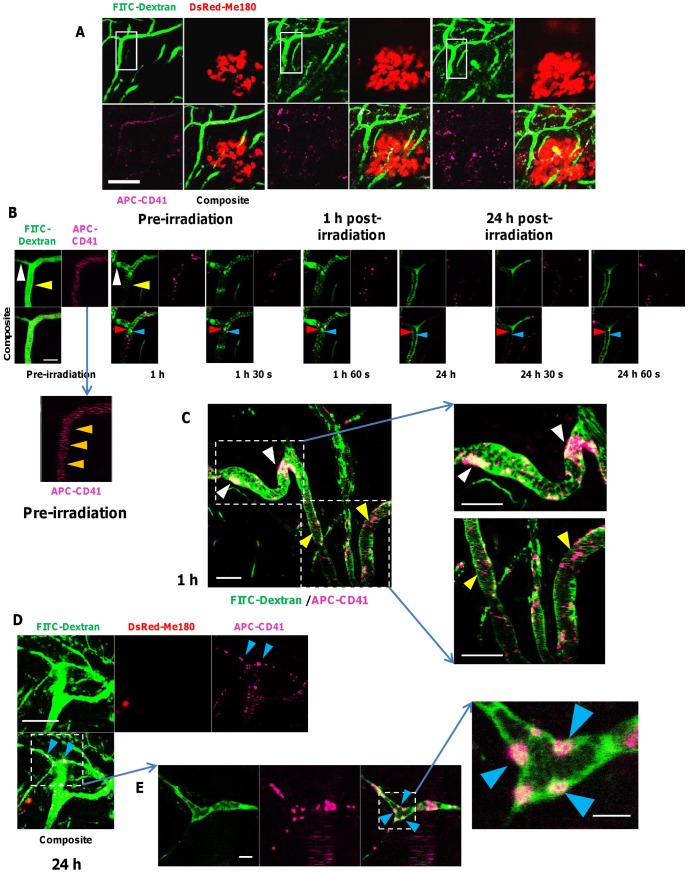
Figure 5. Real-time intravital optical tracking of radiation-induced platelet thrombus formation in tumor microvascular in vivo.
A. FITC-Dextran (green) and APC-labeled anti-mouse CD41 antibodies (fuchsia) were used to visualize tumor microvasculature and platelets, respectively, in relation to the DsRed-Me180 tumor cells (red) before and (1 and 24 h) after a single fraction of 30 Gy. Blood flow is from top to bottom of images. B. Intravital fluorescence imaging (inset of panel A) taken pre-irradiation, 1 h and 24 h after irradiation, with serial images taken consecutively at 30 sec intervals, demonstrating transient formation of platelet thrombi. In pre-irradiation images, fast-moving blood cells, FITC-Dextran and APC-CD41 can be observed as horizontal lines (orange arrows, inset of pre-irradiation images in panel B) in the confocal fluorescence angiograms, as they pass out of the confocal scanning area faster than the image acquisition time (∼15 sec/channel). Compared to pre-irradiation, blood vessel dilation and blockage (white arrow, B), and impeded blood perfusion (yellow arrow, B) were seen 1 h after irradiation in some vessels when platelet thrombi form. Optical tracking of adhered FITC-Dextran-labeled RBCs (red arrows, B) and APC-CD41-labeled thrombotic plaques (blue arrow, B) formed early (1 h) after irradiation but clear after 24 h. After 24 h, early forming thrombi adhered to vessels walls were cleared in many cases. C. Microvascular function was compromised as early as 1 h after radiation by blockages caused mostly by larger (∼20–40 µm diameter) platelet thombi (white arrow, C), while microthrombi (∼2–5 µm diameter) transiently adhered to vessel walls. D. Typically, smaller vessels (∼12 µm diameter) were more prone at 1 and 24 h post-irradiation to thrombosis-induced occlusion (blue arrows, D) than larger (∼25 µm diameter) vessels where small thrombi forming at the vessel wall eventually cleared. E. Confocal fluorescence microscopy also revealed FITC-Dextran labeled RBCs aggregating with platelet thrombi to occlude capillaries, and in many cases adhering to microvessel walls (blue arrows in inset, E). Scale bars: 125 µm (A), 25 µm (B), 50 µm (C), 125 µm (D), 25 µm (E) and 6 µm (inset, E).