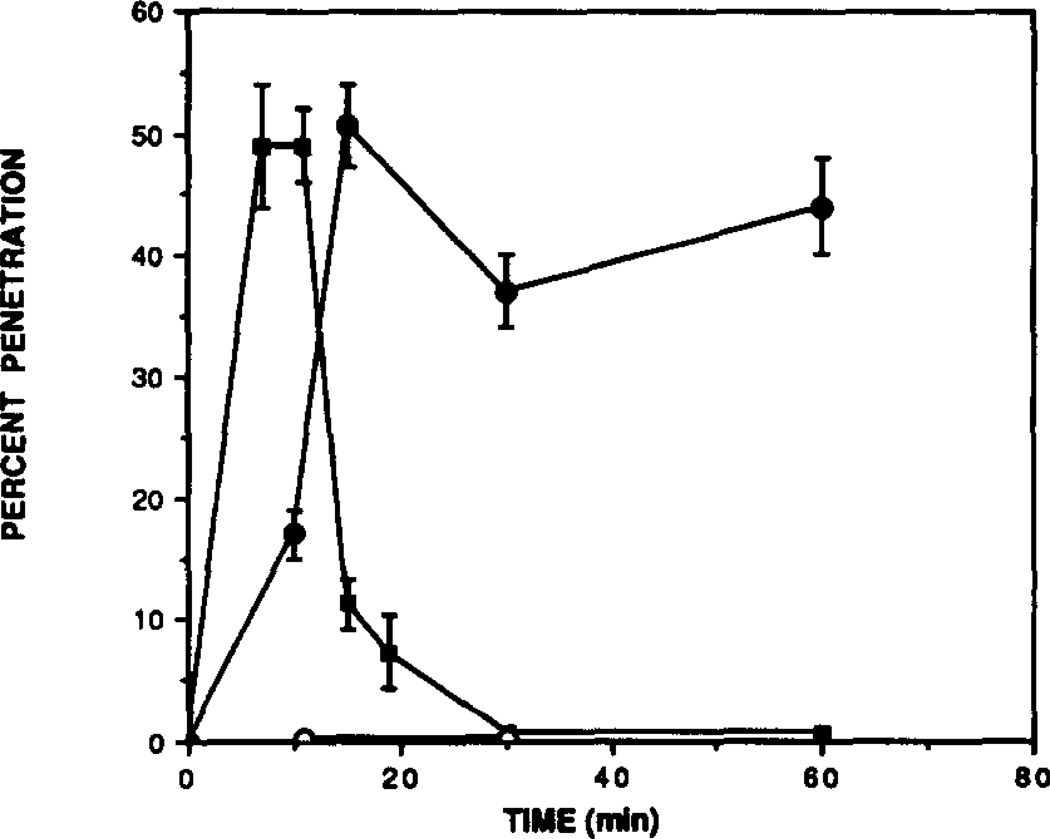
Fig. 3.
Time course for penetration of xanthines in the mouse brain. Mice were injected i.p. with: (■] CPT, 25 mg/ kg; (●) CPX, 0.25 mg/kg; and (○) 8-PST, 50 mk/kg. After the indicated time, their forebrains were removed, homogenized in 8 vol. of Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, and, after treatment with ADA (6 U/mL) used directlfy for [3H]PIA binding. Concentrations of xanthines in brain were determined by comparing [3H]PIA binding to that from a standard curve. One hundred percent brain penetration is defined as the amount of compound reaching the brain in the absence of any permeability barrier assuming that the injected dose distributes uniformly throughout the mouse. Each determination is the mean ± SD from at least three different animals.