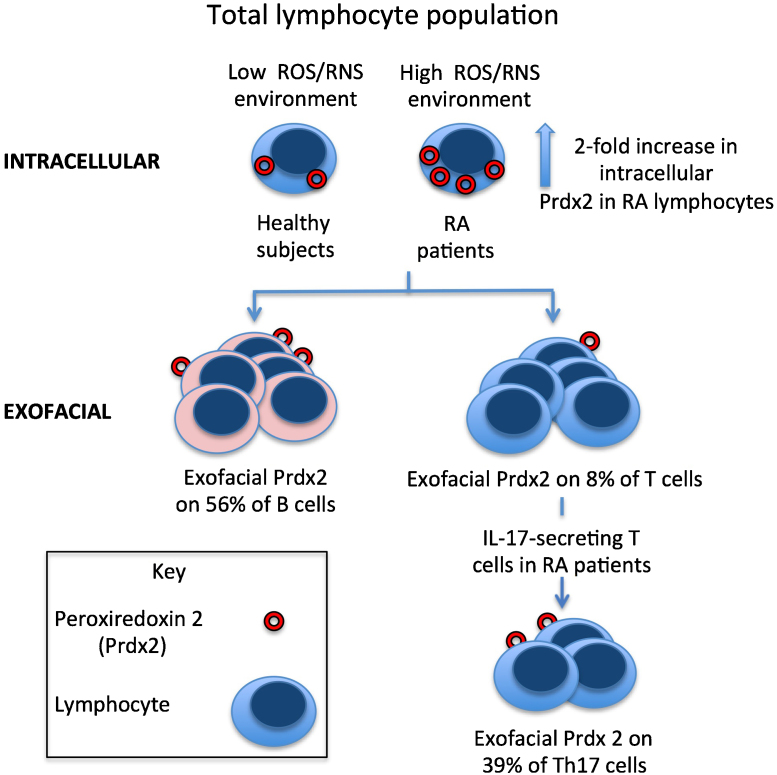
Fig. 5.
A basic summary of some of the major lymphocyte subsets in relation to the levels of intracellular and exofacial Prdx2. The diagram summarizes the key results found in the present study, comparing healthy subjects with RA patients. For simplicity, a number of subtypes of T cell have been omitted from the figure. Prdx2 is schematically shown as a red ring, representing the crystal structure of the decameric human red blood cell Prdx 2 (Schröder et al., 2000). It is unknown if the exofacial Prdx2 is in the decameric, or a different oligomeric form. Intracellular Prdx2 protein content was elevated in RA lymphocytes compared with lymphocytes from healthy subjects. The median proportion of B cells displaying exofacial Prdx2 and Trx1 was higher compared with Prdx2+ve and Trx1+ve T cells in both the RA and healthy subjects. The indicated values of 56% Prdx2+ve B cells and 8% Prdx2+ve T cells are median values of percentages obtained from all the analysed PBL preparations (n = 10; made up of the pooled values from the 5 RA patients and 5 healthy subjects shown in Fig 3B). The medain proportion of Th17 cells displaying exofacial Prdx2 was higher compared with the medain proportion of Prdx2+ve cells in the total lymphocyte population in RA patients. (Th: T helper cell).