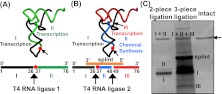
FIGURE 2.
Construction of modified tRNA. (A) Schematic illustration of two-piece ligation. The 5′ fragment (fragment I; black) and the 3′ fragment (fragment II; green) were transcribed by T7 RNA polymerase, using molar excess of dGMP as the initiation nucleotide for fragment II. These two fragments were ligated with T4 RNA ligase 1 to construct a full-length tRNA. (B) Schematic illustration of three-piece ligation. The 5′ fragment (fragment I; black) and the 3′ fragment (fragment III; red) were transcribed by T7 RNA polymerase. The middle piece (fragment II; blue) with the modification was chemically synthesized. These three fragments were ligated with T4 RNA ligase 2 with the assistance of a DNA splint oligonucleotide to construct a full-length tRNA. Note that the actual sites of ligation vary depending on the sequence. See Materials and Methods for details. The red circle in A and B indicates the modified position 37. (C) Denaturing gel analysis of the ligated product. Individual fragments are indicated, except for fragment II in the three-piece ligation, which is too small for the gel analysis. Both the two-piece and three-piece ligation mixtures yield a product that migrates to the same position as the intact tRNA.