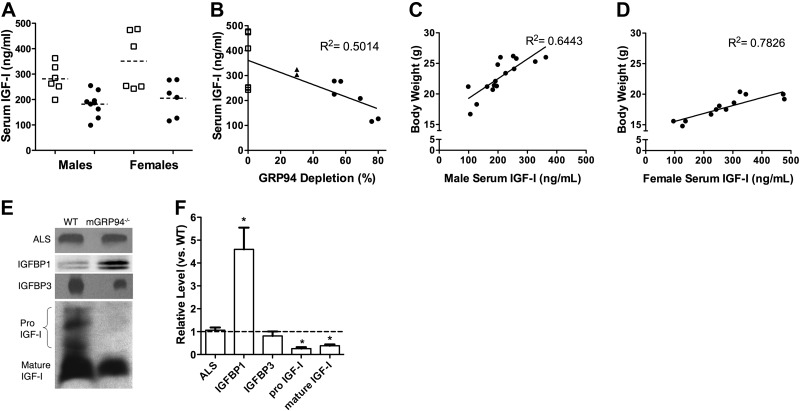
Figure 6.
Effect of GRP94 deletion on serum IGF-I levels. A) Serum IGF-I levels in 8-wk-old male or female mice. ■, WT mice; ●, mGRP94−/− mice. Each point represents an individual mouse, whose IGF-I was measured by ELISA. Horizontal dashed lines are the means of each group of values. Mean serum values for mGRP94−/− mice are significantly lower than serum IGF-I values for sex-matched WT mice by unpaired t test. B) Serum IGF-I levels as a function of GRP94 deletion in the muscles. Each point is the IGF-I value determined by ELISA from an individual mouse and the corresponding GRP94 deletion determined by immunoblotting. ▲, mice heterozygous for both Cre and loxP. C, D) Body weight of 8-wk-old mGRP94−/− mice as a function of their serum IGF-I levels. Each point is an individual animal and shows a high correlation between body weight and circulating IGF-I for both males (C) and females (D). E, F) Comparison of ALS, IGFBP1, IGFBP3, and IGF-I levels in sera from WT and mGRP94−/− mice. E) Immunoblot. F) Quantification of data. IGFBP1 is elevated in the mGRP94−/− serum, whereas there is no significant change in the levels of IGFALS or IGFBP3. IGF-I levels are diminished in the mGRP94−/− serum, with a marked decrease in both mature and pro-IGF-I.