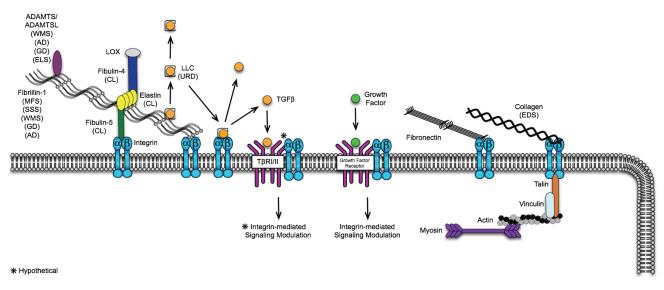
Figure 2.
Extracellular matrix proteins influencing TGFβ and other pathways in disease. Disorders caused by a mutated gene product are shown in brackets next to the protein. Cells sense stiffened matrix through integrin-mediated bridging of ECM proteins (e.g. fibrillins, fibronectin, and collagens) to the cytoskeleletal proteins such as actin and myosin. Integrins can also modulate intracellular signaling via interactions with growth factor receptors (e.g. VEGFR, PDGFR, and IGFR). Diseases: MFS: Marfan syndrome; SSS: Stiff skin syndrome; WMS: Weill-Marchesani syndrome; ELS: Ectopia lentis syndrome; GD: Geophysic dysplasia; AC: Acromelic dysplasia; CL: Cutis Laxa, EDS: Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. *Hypothetical.