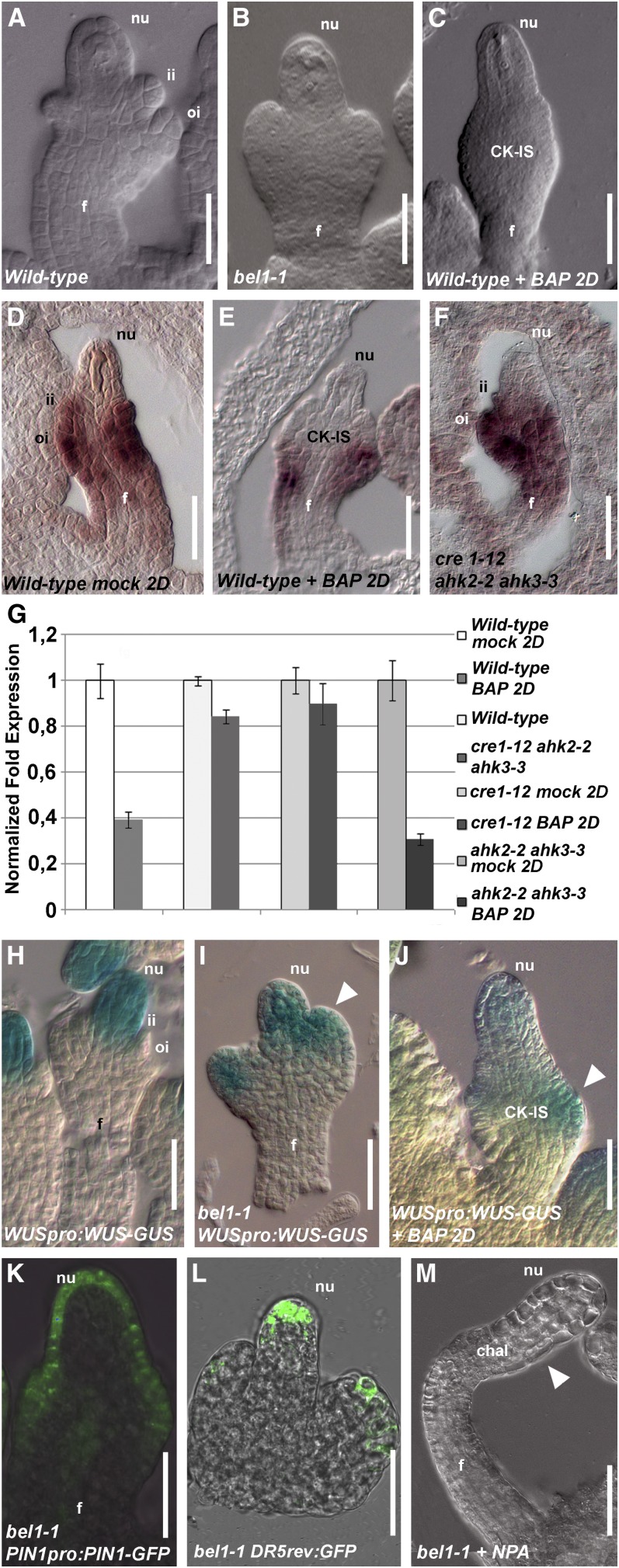
Figure 5.
BEL1 Expression Is Regulated by Cytokinin.
(A) Wild-type ovule, stage 2-III.
(B) bel1-1 ovule, stage 2-III.
(C) Wild-type ovule, stage 2-III, 2 d (2D) after BAP treatment.
(D) In situ hybridization on wild-type ovule with BEL1 probe.
(E) In situ hybridization on wild-type ovule treated with BAP using the BEL1 probe 2 d after treatment.
(F) In situ hybridization on cre1-12 ahk2-2 ahk3-3 triple mutant ovule with BEL1 probe.
(G) Quantitative BEL1 expression analysis by real-time RT-PCR. Wild-type mock-treated or BAP-treated 2 d after treatment, wild-type and cre1-12 ahk2-2 ahk3-3 triple mutant flowers, cre1-12 single mutant, and ahk2-2 ahk3-3 double mutant 2 d after mock treatment or BAP treatment.
(H) to (J) WUSpro:WUS-GUS activity in wild-type ovule (H), bel1-1 ovule (I), and in a wild-type ovule 2 d after BAP treatment (J). The ovules are at stage 2-III/3-I. The white arrowhead indicates ectopic WUSpro:WUS-GUS expression in the aberrant structures of the ovules ([I] to [J]).
(K) PIN1pro:PIN1-GFP in bel1-1 ovule.
(L) DR5rev-pro:GFP in bel1-1 ovule. The ovule is at stage 2-III.
(M) bel1-1 ovule treated with NPA. The arrowhead indicates the region where the bel1-1 structure is formed.
chal, chalaza; f, funiculus; ii, inner integument; nu, nucellus; oi, outer integument.
Bars = 20 μm.