Figure 1.
Preparation of Transgenic Arabidopsis Lines Expressing phyA/phyB Chimeric Proteins.
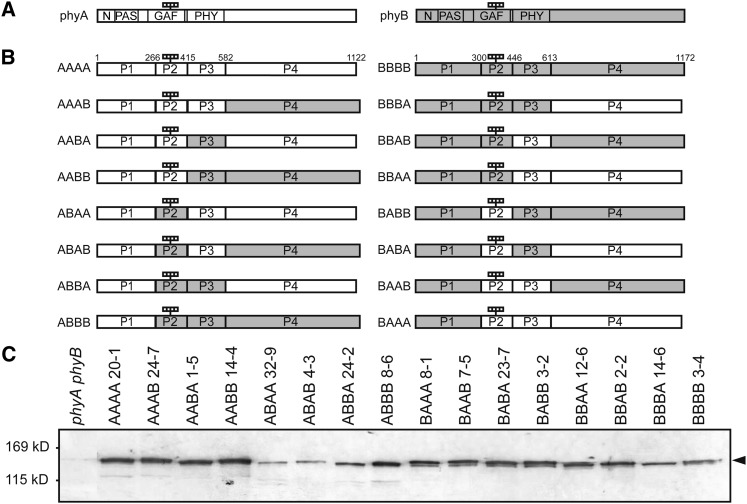
(A) Diagram of phyA and phyB. White and gray boxes indicate the phyA and phyB sequences, respectively. N, N-terminal extension (1 to 78 in phyA; 1 to 102 in phyB); PAS, PAS domain (79 to 185 in phyA; 103 to 219 in phyB); GAF, GAF domain (218 to 402 in phyA; 252 to 433 in phyB); PHY, PHY domain (413 to 593 in phyA; 444 to 624 in phyB). The four small rectangles indicate the chromophores.
(B) Diagram of 16 phyA/phyB chimeric proteins. The phyA and phyB molecules were divided into four parts, and their respective sequences were shuffled between phyA and phyB. Numbers shown on the AAAA and BBBB sequence denote the amino acid positions of the borders. The four rectangles indicate the chromophores.
(C) Immunoblot detection of the phyA/phyB chimeric phytochromes with a mouse monoclonal anti-GFP antibody in etiolated seedlings of representative transgenic lines. Five micrograms of crude protein extract was loaded in each lane.