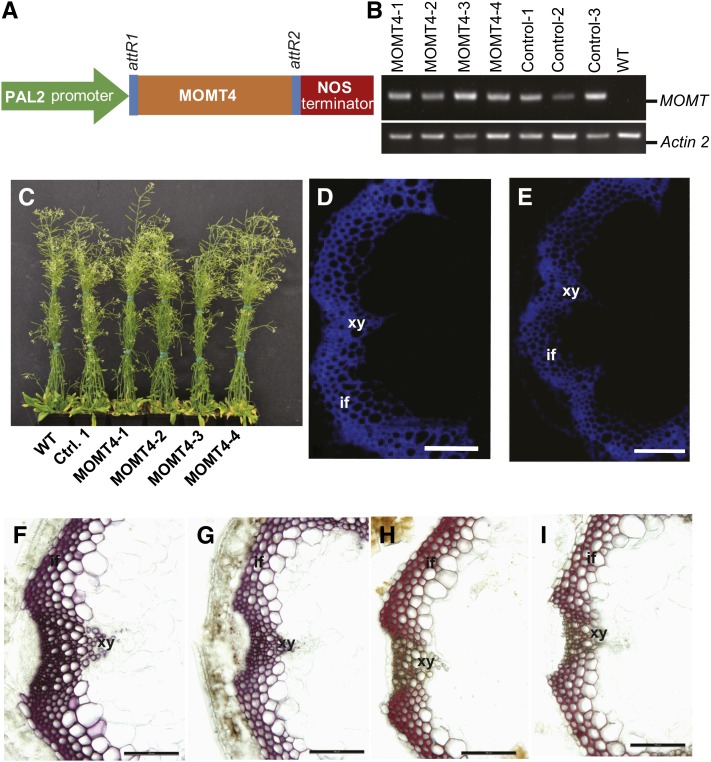
Figure 3.
Expression of MOMT4 in Arabidopsis and Histochemical Analysis of Transgenic Plants.
(A) MOMT4 overexpression cassette driven by a bean Phe ammonia lyase promoter.
(B) RT-PCR analysis on the transgenes of MOMT4 and loss-function variant IEMT (E165R); both transgenes were expressed in the selected transgenic lines.
(C) Morphological phenotype of wild-type, control, and MOMT4 expression plants. WT, the wild type.
(D) UV autofluorescence of a stem section from the first node of a 10-week-old Arabidopsis control plant. if, interfascicular fiber; xy, xylem.
(E) UV autofluorescence of a stem section from the first node of a 10-week-old MOMT4-3 transgenic line.
(F) Phloroglucinol-HCl staining of a stem section from the second basal node of the control line, which indicates the total lignin in violet-red.
(G) Phloroglucinol-HCl staining of a stem section from the second basal node the MOMT4-3 transgenic line.
(H) Mӓule staining of a stem section from the second basal node of a control plant. The staining indicates syringyl lignin subunit in red.
(I) Mӓule staining of a stem section from the second basal node of a MOMT4-3 transgenic plant.
Bars = 50 µm