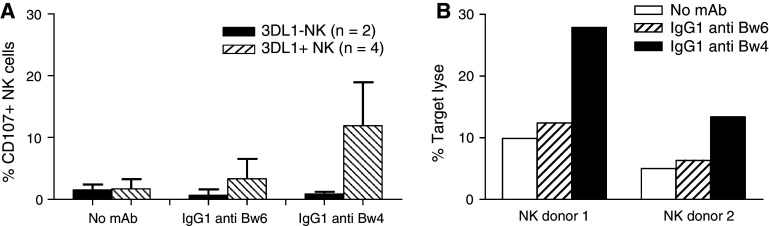
Fig. 2.
Increase by HLA-Bw4-specific mAb MUS4H4 of the susceptibility of high HLA-Bw4-expressing B-CLL cells to NK cell-mediated lysis. a Percentage of CD107+ NK cells from KIR3DL1-positive (n = 4) (stripped bars) and KIR3DL1 negative (n = 2) (black bars) donors following incubation with B-CLL cells in the absence or in the presence of saturating amounts of HLA-Bw4-specific mAb MUS4H4 (IgG) or HLA-Bw6-specific mAb OUW4F11 (IgG). Polyclonal NK cells were isolated and incubated with B-CLL cells at the E:T ratio of 1:2. Error bars indicate standard deviation (SD) b lysis of B-CLL cells by NK cells from two 3DL1-positive donors in the absence (white bars) or in the presence of HLA-Bw4-specific mAb MUS4H4 (IgG) (black bars) or HLA-Bw6-specific mAb OUW4F11 (IgG) (stripped bars). Polyclonal NK cells were isolated and incubated with B-CLL cells at the E:T ratio of 1:10. NK cells were pre-incubated with 50 μl heat-inactivated human AB serum to minimize ADCC