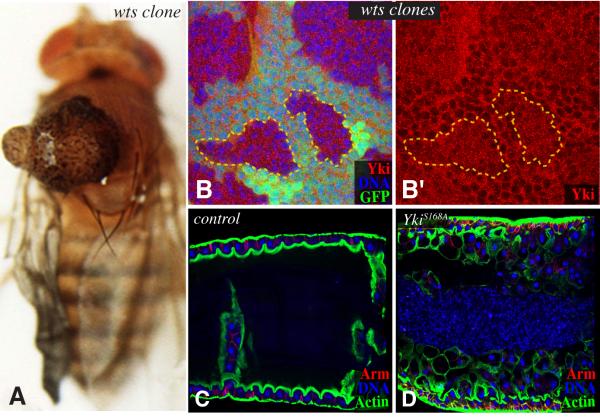
Figure 2. Examples of Hpo pathway phenotypes.
A) Adult fly with a wts mutant clone in the notum, resulting in a tumorous overgrowth (image courtesy of Tian Xu, see (Xu et al., 1995) for details). B) Portion of a wing imaginal disc with wts mutant clones, identified by lack of green staining; two examples are outlined by dashed lines. In wild-type cells, Yki (red) is predominantly cytoplasmic), but in wts mutant cells it is readily detected in the nucleus, resulting in uniform distribution of Yki (reproduced from Oh and Irvine, 2008). Panel B’ shows only the Yki stain. C) Close-up of the intestine of an adult fly. D) Close-up of the intestine of an adult fly in which an activated form of Yki (YkiS168A) is expressed within the differentiated cells. This stimulates an overproliferation of ISCs, and results in a massive overgrowth of the intestine (reproduced from Staley and Irvine, 2010).