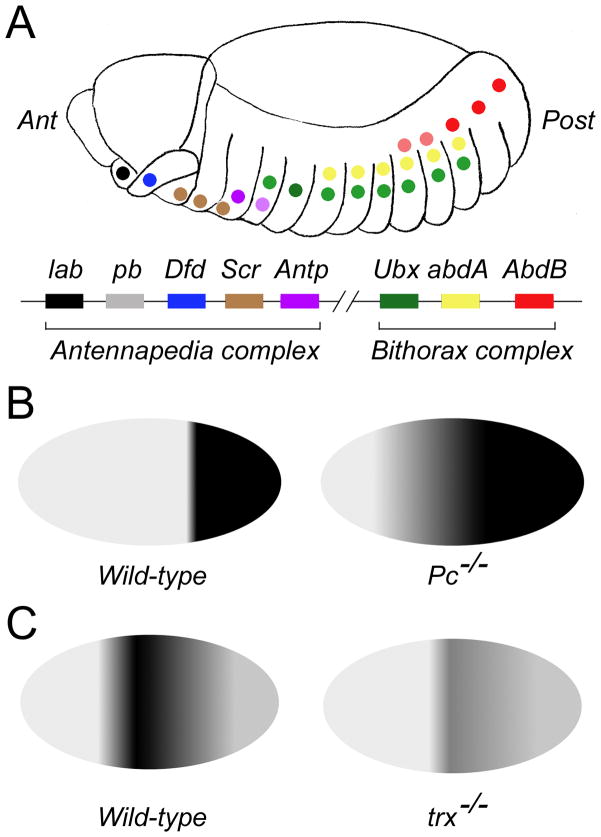
Figure 2. Regulation of Hox genes expression by PcG and TrxG genes in Drosophila.
(A) Staggered expression of Drosophila Hox genes along the anterior-posterior axis of the embryo. The Drosophila genome contains seven Hox genes arranged in two clusters: the Antennapedia complex and the Bithorax complex. The genes and their respective expression domains in the Drosophila embryo are color-coded in this diagram. Ant: anterior; Post: posterior. (B) PcG genes are required to repress Hox genes outside their normal expression domains. The diagram shows expression domain of the Hox gene AbdB in wild-type (left) vs. Pc−/− (right) embryos. AbdB is normally expressed in the posterior segments of wild-type embryos but expands anteriorly in Pc−/− embryos. (C) TrxG genes are required to maintain Hox gene expression. The diagram shows expression of the Hox gene Ubx in wild-type (left) vs. trx−/− embryos (right). Ubx expression is greatly reduced in trx−/− embryos.