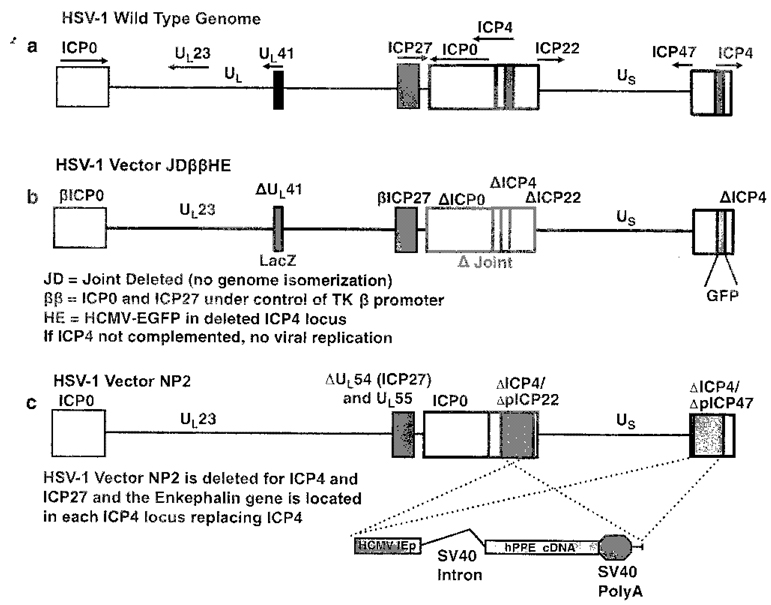
Figure 1.
Replication defective herpes simplex virus (HSV) vector designs. (a) Configuration of wild-type (WT) HSV 1 genome. The boxes represent inverted repeats flanking the unique long (UL) and unique short (US) genome elements. The joint region separates UL, and US. The essential immediate early (IE) genes are ICP27 and ICP4. ICP0, ICP22 and ICP47 are nonessential IE genes. ICP4 and ICP0 are diploid in the genome because they are located in inverted repeat regions. The viral thymidine kinase (tk) gene and the virus host shut-off function (vhs) are located in the U1, segment. All of these genes are manipulated or deleted to create vectors. Deletion of ICP4 and ICP27 render the virus highly replication defective whereas deletion of the nonessential JE genes can compromise the virus life cycle in vivo but do not prevent virus replication in cell culture. (b) Configuration of the JDββHE. This vector is deleted for ICP4 and replaced by the reporter gene GFP. The vector is deleted for the joint region removing ICP4 and ICP0. The vhs gene is deleted and replaced by the reporter gene expression cassette LacZ. The remaining copy of ICP0 and the IE gene ICP27 have their IE gene promoters replaced by the early (E) tk gene promoter limiting their expression to early gene kinetics and are not expressed unless the essential IE gene ICP4 is complemented in engineered Vero cells. This type of vector can be used to express genes in embryonic stem cells. (c) Configuration of the pain vector NP2 employed to treat chronic pain. This vector is deleted for ICF27, ICP4, ICP47 and ICP22. The therapeutic gene preproenkephalin is present in two copies replacing both ICP4 loci.