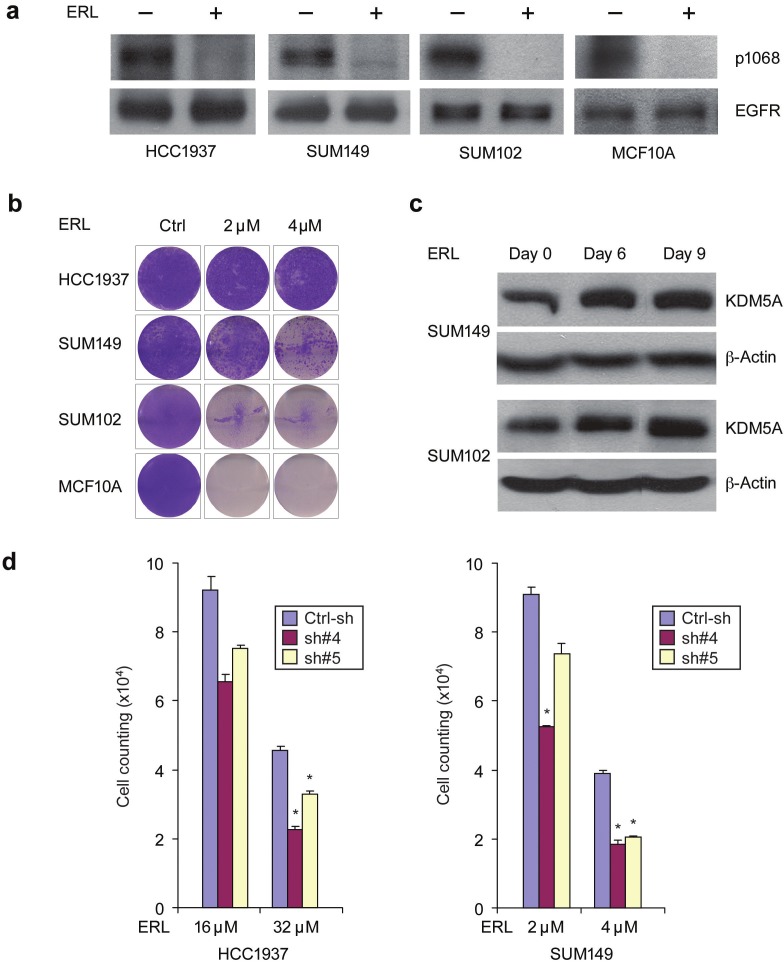
Figure 3.
KDM5A is associated with breast cancer drug resistance. (A) EGFR inhibitor erlotinib (ERL) suppressed EGFR kinase activity in HCC1937, SUM149 and SUM102 breast cancer cell lines and MCF10A control line. Cells were treated with 4 μM erlotinib or vehicle for 1 hour. Protein extracts were immunoblotted with anti-phospho-EGFR (Tyr1068) and anti-EGFR antibodies. (B) Breast cancer cell lines HCC1937, SUM149 and SUM102 as well as the control MCF10A line were plated and left either untreated (Ctrl) or treated with 2 and 4 μM erlotinib for 30 days. Cells were fixed and stained with Crystal Violet or counted. Each experiment was performed in triplicate, and a representative image is presented. (C) Drug-tolerant subpopulation of SUM149 and SUM102 cells had increased KDM5A expression. Cells were plated and treated with 4 μM erlotinib for 6, 9 and 30 days with media/drug changes every two days and then isolated total RNA and protein. Protein extracts were immunoblotted with a KDM5A antibody. (D) KDM5A knockdown reduced the number of drug-tolerant cells in SUM149 and HCC1937. Stable KDM5A-knockdown and control HCC1937 and SUM149 cells were treated with the indicated concentration of erlotinib for 30 days. Cell counting was shown as the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations (*P<0.05 and ** P<0.01, Student’s t test)