Figure 4.
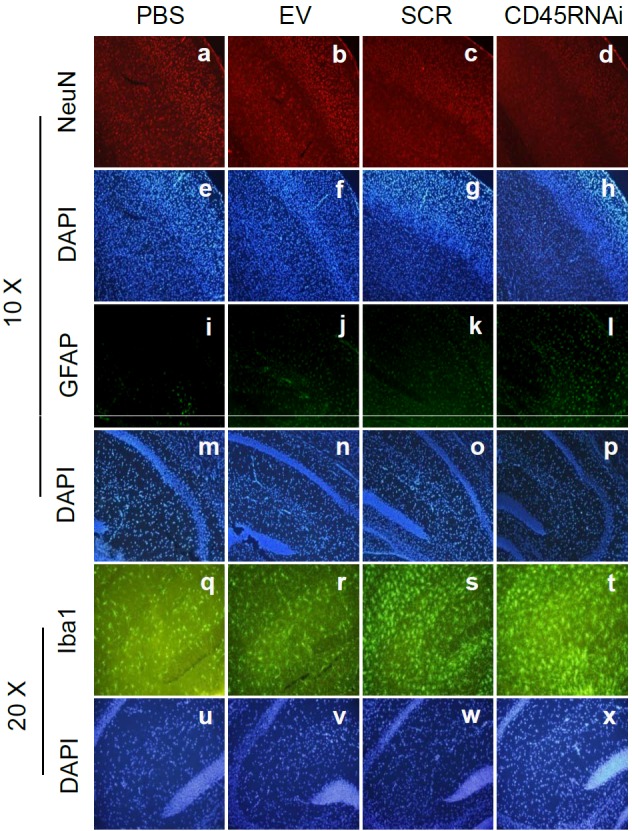
HIV-1 Tat was promoted neuronal death/damage and gliosis in stable knock down CD45 mouse brain detected by immunofluorescence. CD45 knock-down was performed by stable transfection of CD45shRNA into 3-month-old C57BL/6L mice brain (CD45 RNAi) by ICV injection; as controls, empty victor (EV), scrambled shRNA (SCR), and PBS were ICV injected to mouse brain, respectively (n=3 for each group). Subsequently, each mouse from four groups was injected 500 ng of HIV-1 Tat by ICV. Sections from a half-brain were stained by immunofluorescence of NeuN (a-d; for DAPI, e-h; 10 ×), GFAP (i-l; for DAPI, m-p; 10 ×) and Iba1 (q-t; for DAPI, u-x; 20 ×). HIV-1 Tat exacerbated neuronal loss in CD45 knock-down mouse brain sections in cortex (d/h) compared with other controls (a-c/e-g). Further, HIV-1 Tat injection augmented astrocytosis as determined by GFAP staining (i/p) compared with control groups (i-k/m-o). Finally, HIV-Tat injection was increased in microglial expression visualized by Iba1 staining in CD45 knock down mice (t/x) vs. control groups (q-s/u-w) in hippocampus.
