Figure 5.
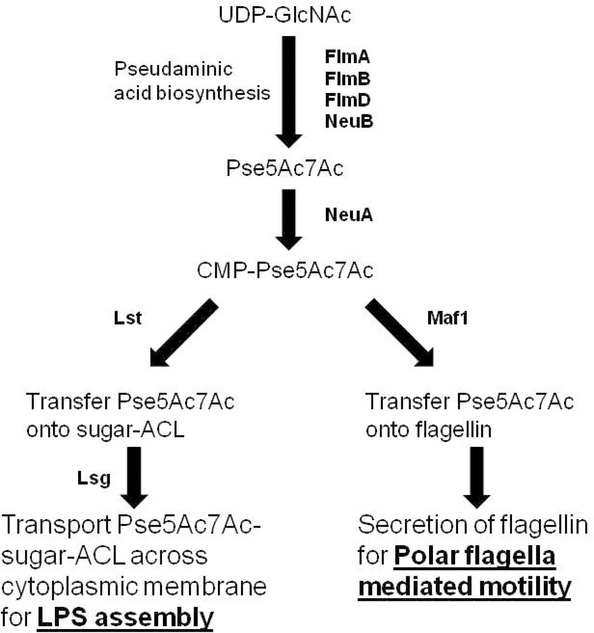
Hypothetical pathway for flagellin glycosylation and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) modification in Aeromonas caviae Sch3N. The biosynthetic pathway to Pse5Ac7Ac is based on the predicted functions of the A. caviae proteins compared with those elucidated for Campylobacter jejuni and Helicobacter pylori proteins (McNally et al. 2006; Schoenhofen et al. 2006). Following biosynthesis of Pse5Ac7Ac by the FlmABD and NeuB, Pse5Ac7Ac is activated by covalent linkage to CMP with NeuA. CMP-Pse5Ac7Ac is then either transferred onto the flagellin by Maf1, which we predict to be a polar flagellin specific glycosyltransferase, or transferred onto a sugar-antigen carrier lipid (ACL) by Lst to create an LPS O-antigen unit, and this O-antigen unit is subsequently transported across the cytoplasmic membrane by Lsg.
