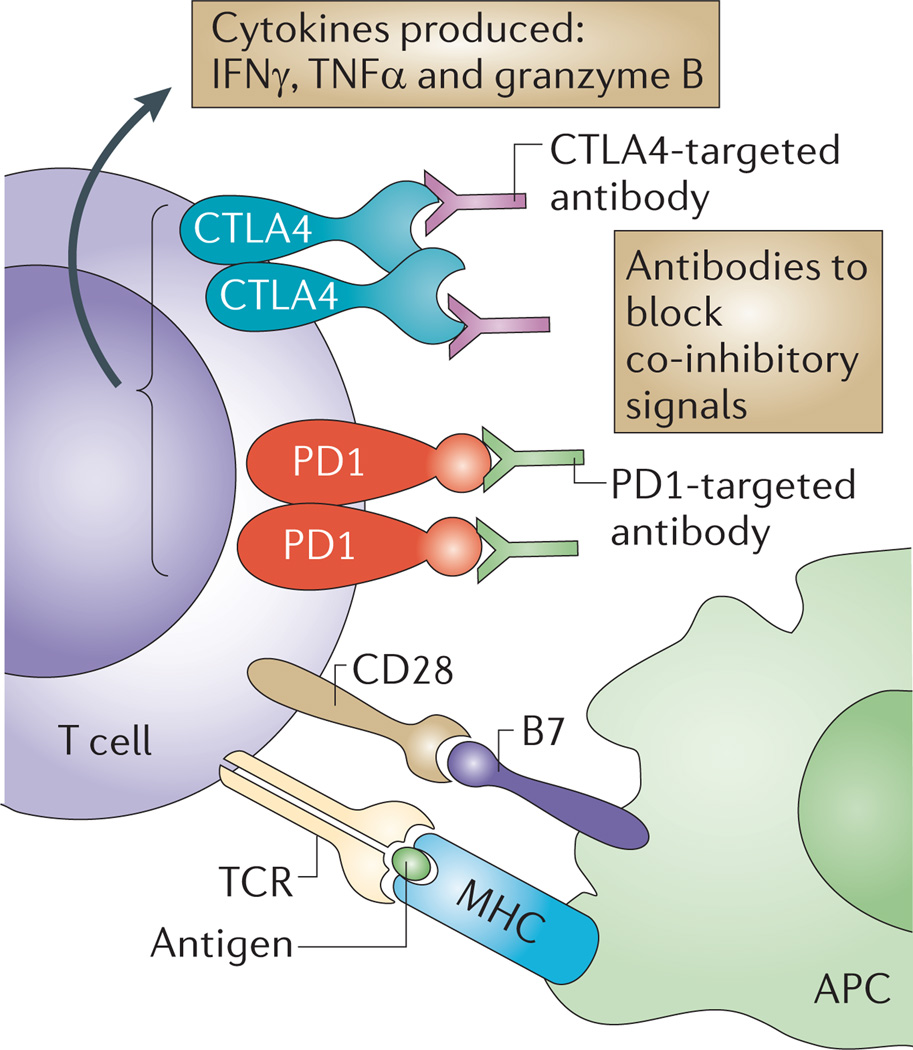
Figure 2. Current therapies that induce effector T cell functions.
Strategies to maintain activated tumour-specific T cells include the use of blocking monoclonal antibodies, such as anti-bodies targeting either cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA4) or programmed cell death 1 (PD1), to neutralize co-inhibitory receptors. Therefore, these antibodies that block intrinsic inhibitory immune checkpoints allow a sustained T cell response, including an increased production of cytokines, such as tumour necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interferon-γ (IFNγ) and granzyme B. APC, antigen-presenting cell; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T cell receptor.