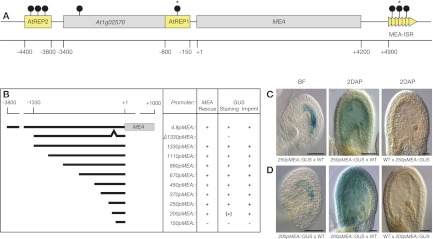
Figure 1.
MEA promoter dissection. (A) The MEA locus contains two helitron transposons, AtREP2 and AtREP1, 5′ of the translational start site and a tandem repeat region, termed MEA-ISR, 3′of the gene. At1g02570 resides in the formerly designated MEA promoter (see also Supplemental Fig. S1). Numbers are relative to the translational start site. (Gray boxes) Genes; (yellow boxes) transposons and repeats; (arrowheads) 182-bp direct repeats; (lollipops) sites of DNA methylation as reported (Xiao et al. 2003; Gehring et al. 2006); (stars) hypomethylation of maternal MEA endosperm alleles at 7–9 d after pollination (DAP). (B) The 4.8pMEA∷MEA transgene contains 3.8 kb of MEA upstream sequence fused to MEA cDNA and was shown to complement the mea-induced seed abortion phenotype (Makarevich et al. 2006). The 4.8pMEA∷GUS transgene was previously described (Spillane et al. 2004) and contains 3.8 kb of MEA upstream sequence plus 1 kb of MEA coding region. The other transgenes consist of 1330-bp to 150-bp MEA promoter sequence fused to MEA genomic DNA (pMEA∷MEA) or the bacterial uidA reporter gene (pMEA∷GUS). In the Δ1330pMEA∷GUS transgene, the region between the −200-bp and −150-bp MEA upstream sequence is deleted. Plus signs [+] indicate positively tested for rescue, staining, or imprinting; minus signs [−] indicate negatively tested for rescue, staining, or imprinting; the plus sign in parenthesis [(+)] indicates deviation from MEA-like GUS staining; and empty fields indicate that the corresponding promoter fusion was not tested. (C,D) Expression of a 250pMEA∷GUS transgene (C) and a 200pMEA∷GUS transgene (D). The transgenes were reciprocally crossed to Ler wild-type plants. Maternal GUS activity is detected with both transgenes before fertilization (BF) and 2 DAP. No paternal GUS activity is detected. For detailed GUS expression analysis, see Supplemental Figure S2. Bar, 50 μm.