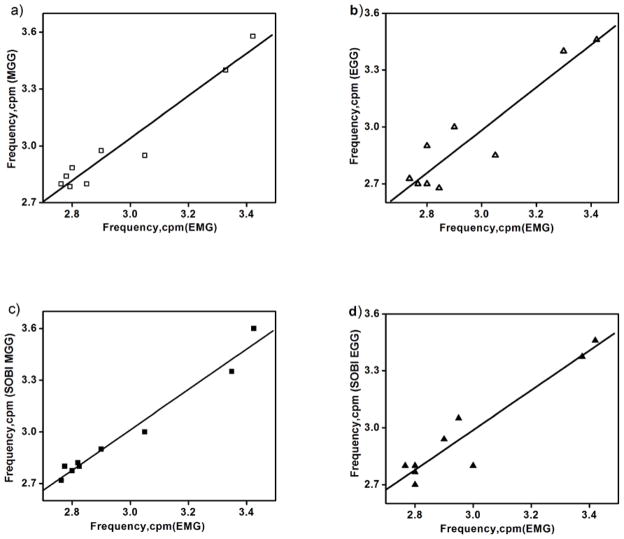
Figure 4.
Correlation between gastric slow wave frequencies recorded by mucosal electrodes (EMG) to those recorded by (a) SQUID magnetometer (MGG), (b) cutaneous electrodes (EGG), (c) SOBI-MGG, and (d) SOBI-EGG. Data points represent peaks detected in FFT of 9 samples of magnetic and electric data. The peak frequencies determined by mucosal electrodes and SQUID are strongly correlated (correlation coefficient, r = 0.97 for EMG/MGG, r = 0.99 for EMG/SOBI- MGG) than between mucosal and cutaneous electrodes (r = 0.93 for EMG/EGG, r = 0.95 for EMG/SOBI- EGG). A linear fit to the data is also shown to emphasize the degree of correlation.