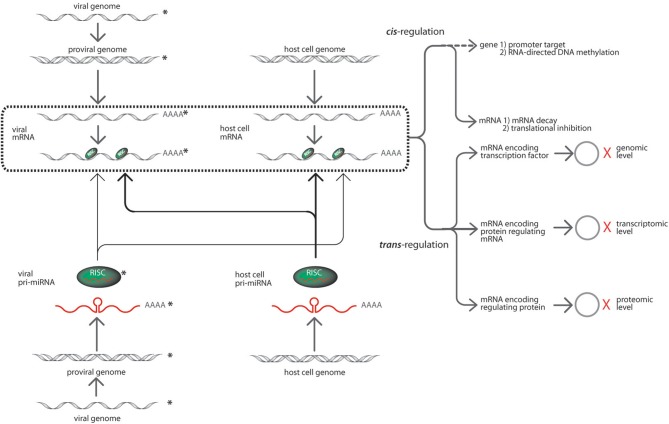
Figure 1.
The prospective targeting interactions of HIV-1 and cellular microRNAs (modified from Cullen, 2006). The interactions among HIV-1 and cellular microRNAs with their corresponding targets may occur in several modules. For instance, HIV-1 encoded microRNAs processed via the host RNAi machinery and incorporated into RISC (in green with the mature microRNA in red) are sourced from HIV-1 pro-viral strands (grey double helix) initially from precursor microRNAs (red lines with poly adenines). These HIV-1 microRNAs can target its viral transcripts or the cellular transcripts. The targeting interactions of microRNAs are shown in solid light arrow lines. In corollary, cellular microRNAs derived from precursor microRNAs (red lines with poly adenines) generated by the host cell genome (grey double helix). The host cellular microRNAs are encoded in the same manner and can target both viral and cellular transcripts where the targeting interactions are shown in solid bold arrow lines. The targeting of mRNA transcripts happens in a highly specific Watson and Crick base-pairing with either complete complementation or seed region complementarity. The box in bold broken lines consolidates all targeting events of the various microRNA-initiated regulatory activities within the systems biology of host-virus interaction. The type of microRNA silencing mechanisms may be grouped as a cis- and trans-regulation event. The cis-regulation event involves microRNA targeting of mRNAs initiating post-transcriptional regulatory responses via mRNA degradation and translational inhibition. Whereas trans-regulation is a tripartite regulatory event which include expression variation of microRNA target genes regulating various viral and cellular activities such as transcription factors, RNA regulatory proteins, interactive genes. The cascades of events cause changes in viral and cellular activities inducing transcriptional regulation, transcriptional variation and protein translational modifications as indicated by the hollow circles = protein products; X (in red) = regulation of expression. The HIV-1 components are distinguished from host cell components with asterisks beside the drawings.