Figure 4. EGF SIGNALING AND WOUND-HEALING RESPONSES.
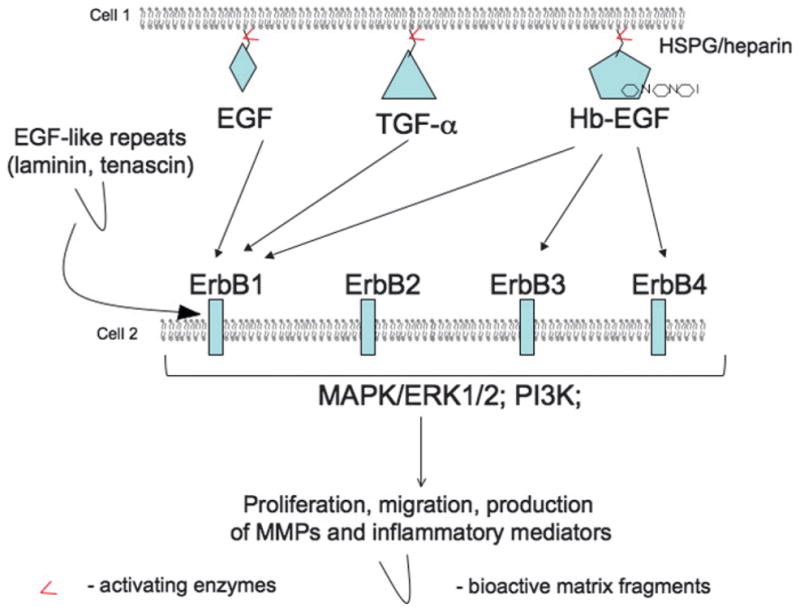
Members of the EGF family are synthesized in a membrane-bound form. Their release from a membrane and activation is performed by matrix metalloproteinases of MMP and ADAM families. Activated epidermal growth factors (EGFs)—EGF, transforming growth factor α (TGF-α), and heparin-binding EGF (HB-EGF)—interact with 1 or more Erb receptors (arrows). Note that Erb2 receptor does not bind EGF ligands and acts as a dimer-forming partner or a coreceptor. Ligand-receptor interactions initiate several signaling pathways, including mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways (MAPK), Erk1/2, and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase leading to increase in post-injury migration, proliferation, and production of MMPs and inflammatory mediators. Interestingly, Erb receptors can be activated by matrix fragments that contain EGF-like repeats.
