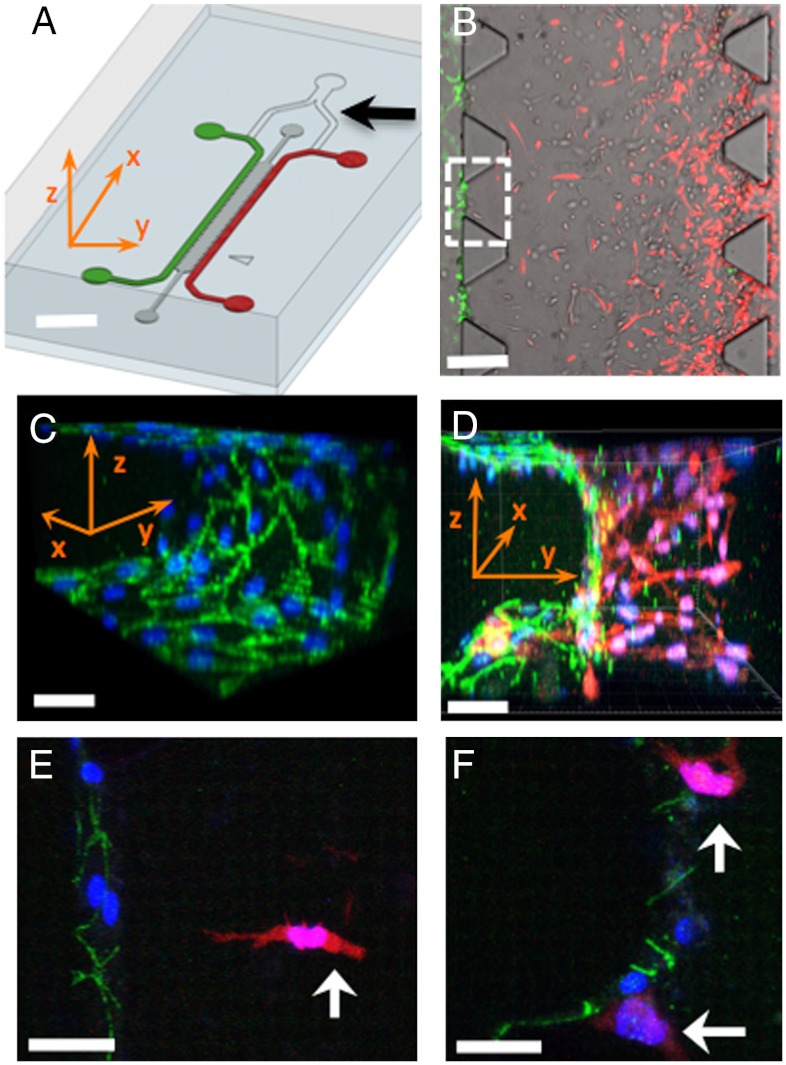
Fig. 1.
Microfluidic tumor-vascular interface model. (A) Endothelial channel (green), tumor channel (red), and 3D ECM (dark gray) between the two channels. Channels are 500 μm wide, 20 mm in length, and 120 μm in height. Black arrow shows the y-junction. (Scale bar: 2 mm.) (B) Phase contrast image showing the fibrosarcoma cells (HT1080, red) invading through the ECM (gray) toward the endothelium (MVEC, green). A single 3D ECM hydrogel matrix region is outlined with the white dashed square. (Scale bar: 300 μm.) (C) VE-cadherin and DAPI staining to show the confluency of the endothelial monolayer on the 3D ECM (outlined with white square in B). (D) Three-dimensional rendering of a confocal z-stack of a single region showing the tumor cells invading in 3D and adhering to the endothelium. (Scale bar: 30 μm.) (E) HT1080 cell (white arrow) invading in 3D toward the endothelium. (Scale bar: 30 μm.) (F) HT1080 cells in contact with the endothelial monolayer. In C–F all scale bars are 30 μm. Green, VE-cadherin; blue, DAPI; red, HT1080-mCherry. x-, y-, z- coordinate indication is appropriately adjusted in A, C, and D.