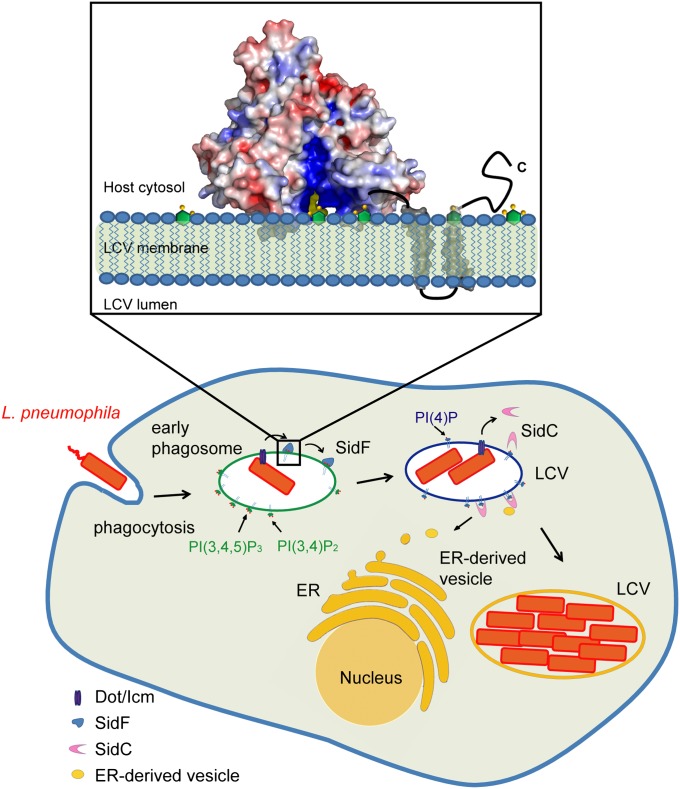
Fig. 6.
Functional model of SidF. The Legionella effector protein SidF is a PI-3-phosphatase that specifically hydrolyzes PI(3,4)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3. By the action of SidF and/or other unknown mechanisms, a PI(4)P enriched LCV membrane is established. PI(4)P enrichment may allow specific anchoring of Dot/Icm effectors, such as SidC, to the LCV, thus facilitates the recruitment and fusion of ER-derived vesicles with the LCV. (Inset) Molecular mechanisms of SidF. SidF anchors on the LCV membrane through its C-terminal double transmembrane motifs. The flat surface of the cytosolic domain of SidF interfaces with the LCV membrane and the two hydrophobic loops protruding out from the flat surface penetrate into the bilayer. The basic charges in the catalytic groove facilitate the loading of substrate into the catalytic site.