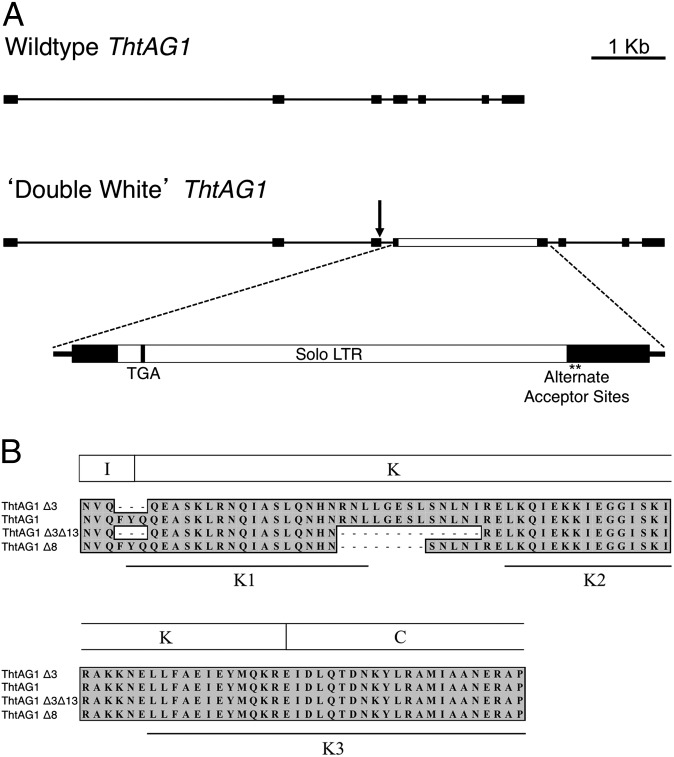
Fig. 4.
Comparative genomic structure of ThtAG1 reveals a retrotransposon insertion in the ‘Double White’ mutant that disrupts mRNA accumulation and protein function. (A) Genomic structure of the ThtAG1 locus in wild-type (Upper) and ‘Double White’ (Lower). Lines represent introns, black boxes represent exons, arrow represents donor site, and the white box represents an insertion. The K domain is roughly encoded by exons 3–5 shown here. A detail of the insertion shows a solo LTR of a retrotransposon coding for an early stop codon (TGA) and two cryptic splice-acceptor sites (asterisks). (B) Translated amino acid alignment of the K-domain region of T. thalictroides wild-type and ‘Double White’ ThtAG1 recovered from cDNA. Note that two ‘Double White’ transcripts that result from the alternate acceptor sites in (A) translate into shorter proteins, lacking either eight or 13 amino acids. The three K subdomains are indicated (50), showing that the missing amino acids in ‘Double White’ affect the area near the end of the K1 subdomain and the region between K1 and K2 subdomains.