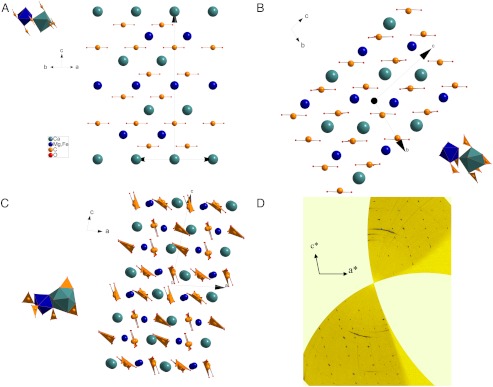
Fig. 1.
(A) The crystal structure of dolomite and (B) dolomite-II. The main difference is in the coordination site of Ca (C.N 6 in dolomite and C.N 7/8 in dolomite-II. (C) The crystal structure of dolomite-III. In this structure, there are 8 nonequivalent cation sites, one half of which are occupied by Ca and the other by (Mg,Fe). The coordination environment is variable (C.N. 7–9), always with larger sites occupied by Ca and smaller by (Mg,Fe). (D) Unwarped reciprocal plane 0kl from experimental data collected at 56 GPa [Blue balls: Ca, green: (Mg,Fe), yellow: carbon].