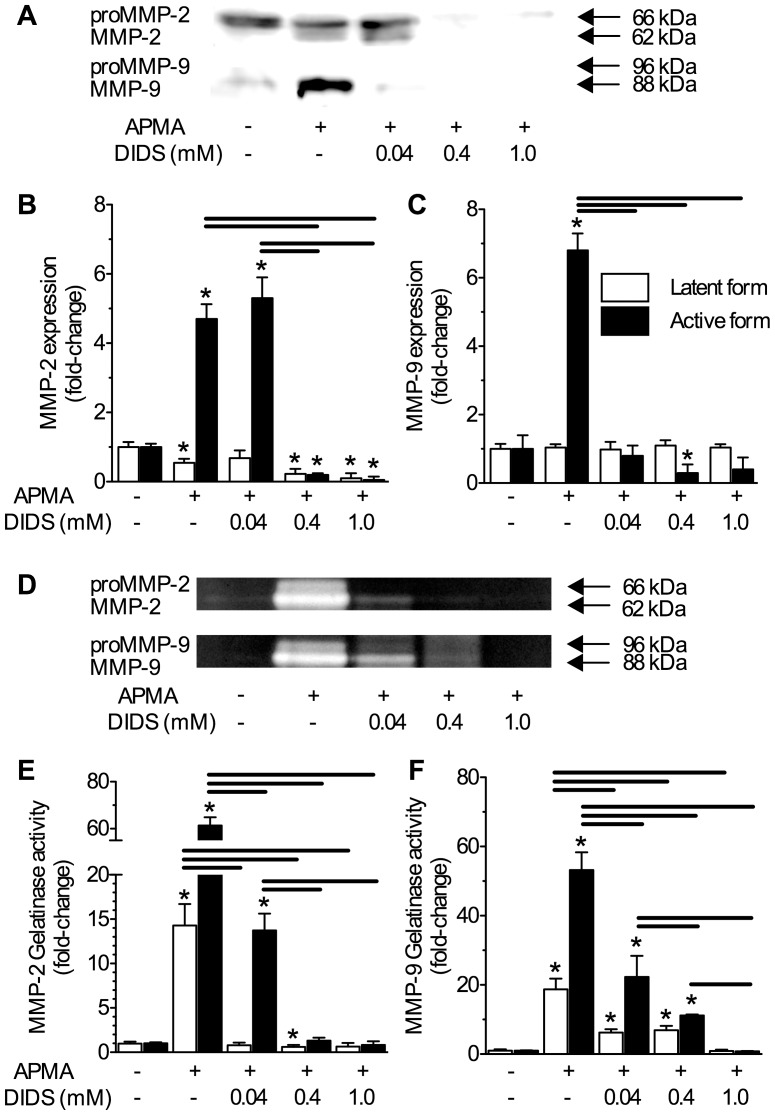
Figure 6. DIDS inhibits APMA-mediated extracellular MMP-2 or -9 protein expression and gelatinolytic activity in a dose-dependent fashion.
Perfusion of the general proteinase agonist 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate (APMA) increases latent and active MMP-2 and active MMP-9 isoform expression and extracellular gelatinolytic activity in the supernatant. Co-treatment with DIDS reduces extracellular MMP protein expression and gelatinolytic activity in a dose-dependent fashion. (A) Sample Western blot of MMP-2 and -9 protein expression, and (B&C) summaries of dose-response relationships of APMA-mediated latent and active MMP-2 (B) and -9 (C) protein isoform expression in supernatant fractions vs. [DIDS] (0.04–1.0 mM), normalized to untreated controls. (D) Sample zymography gel of APMA-mediated latent (white bars) and active (black bars) MMP-2 and -9 isoform gelatinolytic activity vs. [DIDS] of supernatant samples taken from neurons treated as indicated. (E&F) Summaries of latent and active MMP-2 (E) and -9 (F) isoform gelatinolytic activities from (D). Data are presented as mean fold-change relative to untreated controls. Data are mean ±SEM from 3–4 separate 1-hr experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate significant difference from normoxic controls; black bars indicate significance between connected treatments (p<0.05). Treatments as per Fig. 1 caption and 100 µM APMA.