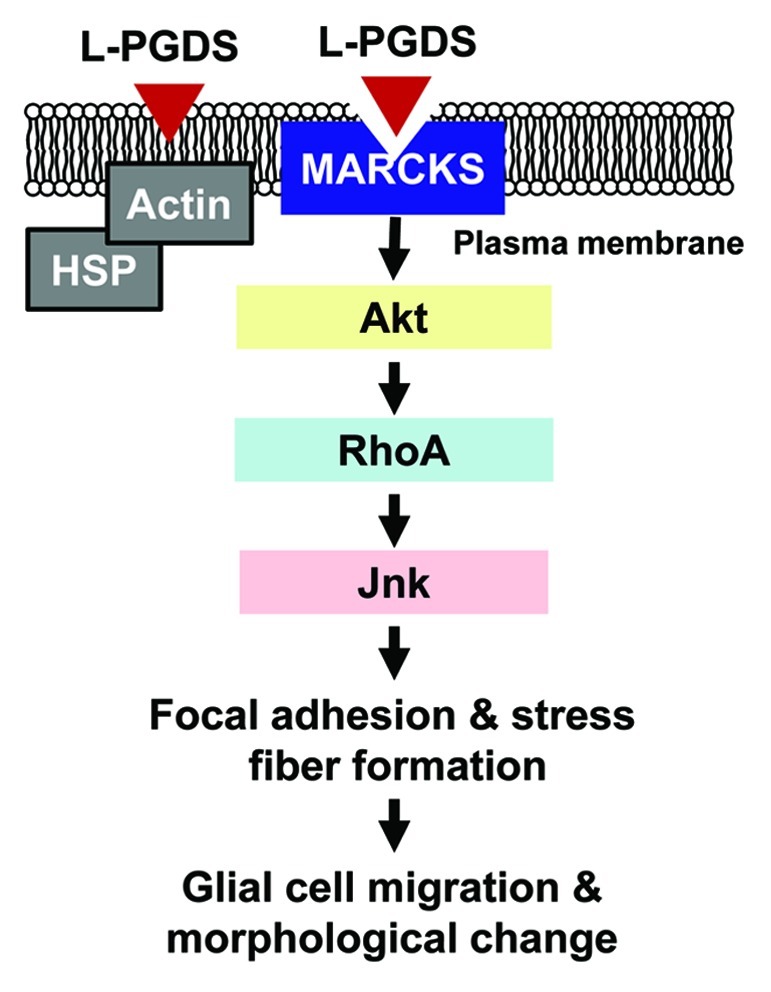
Figure 1. Schematic diagram depicting the L-PGDS-induced glial cell migration and morphological changes. Secreted L-PGDS protein promotes glial cell migration and morphological change by binding to MARCKS protein in plasma membrane. L-PGDS-MARCKS complex may sequentially activate Akt, RhoA, and Jnk, which in turn induces actin polymerization and focal adhesion formation. The effects of L-PGDS under this condition seem to be independent of its enzymatic activity to produce PGD2. Alternatively, L-PGDS may indirectly interact with heat shock proteins (HSP) or actin through membrane-anchoring adaptor proteins. The role of these proteins, however, needs to be further investigated in the future. Adapted from Lee et al.13
